Can anyone explain how to implement one-to-one, one-to-many and many-to-many relationships while designing tables with some examples?
4 Answers
One-to-one: Use a foreign key to the referenced table:
student: student_id, first_name, last_name, address_id
address: address_id, address, city, zipcode, student_id # you can have a
# "link back" if you need
You must also put a unique constraint on the foreign key column (addess.student_id) to prevent multiple rows in the child table (address) from relating to the same row in the referenced table (student).
One-to-many: Use a foreign key on the many side of the relationship linking back to the "one" side:
teachers: teacher_id, first_name, last_name # the "one" side
classes: class_id, class_name, teacher_id # the "many" side
Many-to-many: Use a junction table (example):
student: student_id, first_name, last_name
classes: class_id, name, teacher_id
student_classes: class_id, student_id # the junction table
Example queries:
-- Getting all students for a class:
SELECT s.student_id, last_name
FROM student_classes sc
INNER JOIN students s ON s.student_id = sc.student_id
WHERE sc.class_id = X
-- Getting all classes for a student:
SELECT c.class_id, name
FROM student_classes sc
INNER JOIN classes c ON c.class_id = sc.class_id
WHERE sc.student_id = Y
- 28,463
- 14
- 94
- 146
- 83,810
- 28
- 209
- 234
-
5What's a good example of when the "link back" is useful in the One-to-One relationship? Thanks for the clear and concise answer. – dev_feed May 29 '14 at 15:32
-
3@dev_feed In terms of database design I don't see the link back to be beneficial, but using the example above the link back could simplify finding a `student` given an `address`. – edhedges Sep 06 '14 at 23:23
-
1Each `student_classes` row would have 2 *One-To-One* relationships, right? One `student` row has many classes and one `classes` row has many students -- but one `student_classes` row has only one to each of them (?). – Cody Jul 06 '15 at 16:56
-
2@Cody Each `student_classes` row should only have one one-to-one relationship. If `studentA` is in `classA` and `classB`, then there should be two rows in `student_classes`, one for which relationship. – NullUserException Jul 06 '15 at 16:59
-
15In a one to one relationship, the join field should be unique in both tables. It is likely a PK on one table which guarantees uniqueness, but it may need a unique index on the other table. – HLGEM Apr 14 '16 at 18:54
Here are some real-world examples of the types of relationships:
One-to-one (1:1)
A relationship is one-to-one if and only if one record from table A is related to a maximum of one record in table B.
To establish a one-to-one relationship, the primary key of table B (with no orphan record) must be the secondary key of table A (with orphan records).
For example:
CREATE TABLE Gov(
GID number(6) PRIMARY KEY,
Name varchar2(25),
Address varchar2(30),
TermBegin date,
TermEnd date
);
CREATE TABLE State(
SID number(3) PRIMARY KEY,
StateName varchar2(15),
Population number(10),
SGID Number(4) REFERENCES Gov(GID),
CONSTRAINT GOV_SDID UNIQUE (SGID)
);
INSERT INTO gov(GID, Name, Address, TermBegin)
values(110, 'Bob', '123 Any St', '1-Jan-2009');
INSERT INTO STATE values(111, 'Virginia', 2000000, 110);
One-to-many (1:M)
A relationship is one-to-many if and only if one record from table A is related to one or more records in table B. However, one record in table B cannot be related to more than one record in table A.
To establish a one-to-many relationship, the primary key of table A (the "one" table) must be the secondary key of table B (the "many" table).
For example:
CREATE TABLE Vendor(
VendorNumber number(4) PRIMARY KEY,
Name varchar2(20),
Address varchar2(20),
City varchar2(15),
Street varchar2(2),
ZipCode varchar2(10),
Contact varchar2(16),
PhoneNumber varchar2(12),
Status varchar2(8),
StampDate date
);
CREATE TABLE Inventory(
Item varchar2(6) PRIMARY KEY,
Description varchar2(30),
CurrentQuantity number(4) NOT NULL,
VendorNumber number(2) REFERENCES Vendor(VendorNumber),
ReorderQuantity number(3) NOT NULL
);
Many-to-many (M:M)
A relationship is many-to-many if and only if one record from table A is related to one or more records in table B and vice-versa.
To establish a many-to-many relationship, create a third table called "ClassStudentRelation" which will have the primary keys of both table A and table B.
CREATE TABLE Class(
ClassID varchar2(10) PRIMARY KEY,
Title varchar2(30),
Instructor varchar2(30),
Day varchar2(15),
Time varchar2(10)
);
CREATE TABLE Student(
StudentID varchar2(15) PRIMARY KEY,
Name varchar2(35),
Major varchar2(35),
ClassYear varchar2(10),
Status varchar2(10)
);
CREATE TABLE ClassStudentRelation(
StudentID varchar2(15) NOT NULL,
ClassID varchar2(14) NOT NULL,
FOREIGN KEY (StudentID) REFERENCES Student(StudentID),
FOREIGN KEY (ClassID) REFERENCES Class(ClassID),
UNIQUE (StudentID, ClassID)
);
- 41,009
- 21
- 145
- 105
- 1,891
- 1
- 9
- 2
-
1st example: GID number(6) and SGID Number(4), why? Shouldn't SGID also be (6)? And at 2nd example number(4) and number(2)... – obeliksz Dec 07 '18 at 11:02
-
-
2
-
2@strix25 To enforce avoiding repetition in creating the same ClassStudentRelation row multiple times, because if you don't make sure both foreign keys StudentID and ClassID are unique, what stops creating a new row with the same StudentID and ClassID ? as they are not unique in the code above. So you either implement it like the code above, or add a primary key that includes both StudentID and ClassID to avoid repetition of creating the same row in ClassStudentRelation. – Fouad Boukredine May 04 '19 at 19:18
-
@FouadDev Basically you are saying to strix25 that although we have many to many, between class and student, we should not be able to create (james has biology and biology has james ) more than once. since it already exists. – valik Jun 28 '19 at 07:01
-
1@valik Data in databases work by referencing existing data, and not creating the same piece of data multiple times, why would you do that? of course you don't have to, otherwise it's not efficient. With that in mind, let's go back to your example (james has biology and biology has james), Of course you can, BUT without creating another piece of data that already exist in database. All you need to do is to just reference the already existing one whenever you want to create any relationship. I hope that helps :) – Fouad Boukredine Jul 11 '19 at 23:09
-
Government -> State is not an example for 1:1 relationship because gov may have multiple states so it must be 1:M – Sarvar Nishonboyev Jun 29 '21 at 13:15
-
1@SarvarNishonboyev , `Gov` is for Governor, so Governor -> State is a 1:1 (One Governor is more than enough! ;) ) – Lemmy_Caution Mar 20 '23 at 15:23
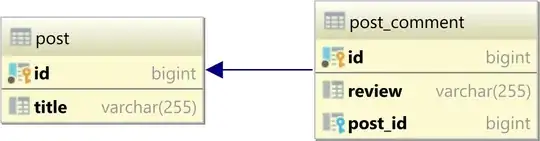
One-to-many
The one-to-many table relationship looks as follows:
In a relational database system, a one-to-many table relationship links two tables based on a Foreign Key column in the child which references the Primary Key of the parent table row.
In the table diagram above, the post_id column in the post_comment table has a Foreign Key relationship with the post table id Primary Key column:
ALTER TABLE
post_comment
ADD CONSTRAINT
fk_post_comment_post_id
FOREIGN KEY (post_id) REFERENCES post
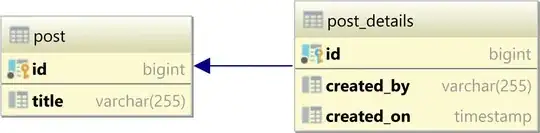
One-to-one
The one-to-one table relationship looks as follows:
In a relational database system, a one-to-one table relationship links two tables based on a Primary Key column in the child which is also a Foreign Key referencing the Primary Key of the parent table row.
Therefore, we can say that the child table shares the Primary Key with the parent table.
In the table diagram above, the id column in the post_details table has also a Foreign Key relationship with the post table id Primary Key column:
ALTER TABLE
post_details
ADD CONSTRAINT
fk_post_details_id
FOREIGN KEY (id) REFERENCES post
Many-to-many
The many-to-many table relationship looks as follows:
In a relational database system, a many-to-many table relationship links two parent tables via a child table which contains two Foreign Key columns referencing the Primary Key columns of the two parent tables.
In the table diagram above, the post_id column in the post_tag table has also a Foreign Key relationship with the post table id Primary Key column:
ALTER TABLE
post_tag
ADD CONSTRAINT
fk_post_tag_post_id
FOREIGN KEY (post_id) REFERENCES post
And, the tag_id column in the post_tag table has a Foreign Key relationship with the tag table id Primary Key column:
ALTER TABLE
post_tag
ADD CONSTRAINT
fk_post_tag_tag_id
FOREIGN KEY (tag_id) REFERENCES tag
- 142,745
- 71
- 566
- 911
-
Hey. I have a question: in many-to-many relationship there is need to set foreign keys as primary keys too? – vallim Apr 11 '21 at 16:16
-
2@vallim In the link table, the PK is a composite of the two FKs. – Vlad Mihalcea Apr 11 '21 at 16:18
One to one (1-1) relationship: This is relationship between primary & foreign key (primary key relating to foreign key only one record). this is one to one relationship.
One to Many (1-M) relationship: This is also relationship between primary & foreign keys relationships but here primary key relating to multiple records (i.e. Table A have book info and Table B have multiple publishers of one book).
Many to Many (M-M): Many to many includes two dimensions, explained fully as below with sample.
-- This table will hold our phone calls.
CREATE TABLE dbo.PhoneCalls
(
ID INT IDENTITY(1, 1) NOT NULL,
CallTime DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE(),
CallerPhoneNumber CHAR(10) NOT NULL
)
-- This table will hold our "tickets" (or cases).
CREATE TABLE dbo.Tickets
(
ID INT IDENTITY(1, 1) NOT NULL,
CreatedTime DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE(),
Subject VARCHAR(250) NOT NULL,
Notes VARCHAR(8000) NOT NULL,
Completed BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 0
)
-- This table will link a phone call with a ticket.
CREATE TABLE dbo.PhoneCalls_Tickets
(
PhoneCallID INT NOT NULL,
TicketID INT NOT NULL
)
- 4,090
- 41
- 39
-
10Would have been better & more clear if you had added primary key and foreign key constraints as well. – Ashish K Gupta Jul 13 '17 at 09:55