SDSL is very mature, with implementations of suffix tree, suffix array, wavelet tree, and many other structures in C++.
"The Succinct Data Structure Library (SDSL) is a powerful and flexible C++11 library implementing succinct data structures. In total, the library contains the highlights of 40 research publications. Succinct data structures can represent an object (such as a bitvector or a tree) in space close to the information-theoretic lower bound of the object while supporting operations of the original object efficiently. The theoretical time complexity of an operation performed on the classical data structure and the equivalent succinct data structure are (most of the time) identical."
A list of structures implemented in SDSL can be found here.
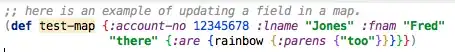
An example of average LCP - longest common prefix search using suffix tree (example from SDSL sources, file text-statistics.cpp):
#include <sdsl/suffix_trees.hpp>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
using namespace sdsl;
typedef cst_sct3<> cst_t;
typedef cst_t::char_type char_type;
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
if (argc < 2) {
cout << "Usage: "<< argv[0] << " file" << endl;
cout << "(1) Generates the CST of file." << endl;
cout << "(2) Calculates the avg LCP value and the runs in the BWT." << endl;
return 1;
}
cst_t cst;
construct(cst, argv[1], 1);
long double runs = 1;
long double avg_lcp = 0;
if (cst.csa.size()) {
char_type prev_bwt = cst.csa.bwt[0];
for (uint64_t i=1; i<cst.csa.size(); ++i) {
char_type bwt = cst.csa.bwt[i];
if (prev_bwt != bwt) {
runs += 1.0;
}
prev_bwt = bwt;
avg_lcp += cst.lcp[i];
}
avg_lcp /= cst.csa.size();
for (size_t k=0; k<=5; k++) {
cout << "H_" << k << ": " << Hk(cst,k).first << endl;
}
cout << "avg LCP: " << avg_lcp << endl;
cout << "runs in BWT: " << runs << endl;
}
}
