The Problem:
When you use session in an ASP.NET site, it causes dramatic delays (multiples of 500ms) when loading multiple requests at nearly the same time.
More Specifically, My Problem
Our website uses session exclusively for its SessionId. We use this key to look up a db table that has user info, etc. This seemed to be a good design since it stored minimal session data. Unfortunately, the SessionId will change if you store nothing in session, so we store Session["KeepId"] = 1;. This is enough to convince SessionId to not change.
On a seemingly unrelated note, the site serves customized product images through a controller action. This action generates an image if needed then redirects to the cached image. This means that one web page may contain images or other resources, sending dozens of requests through the ASP.NET pipeline.
For whatever reason, when you (a) send multiple requests at the same time and (b) have session involved in any way then you will end up with random 500ms delays about 1/2 the time. In some cases these delays will be 1000ms or more, always increasing in intervals of ~500ms. More requests means longer wait times. Our page with dozens of images can wait 10+ seconds for some images.
How to Reproduce the Problem:
- Create an empty ASP.NET MVC Web Application
Create an empty controller action:
public class HomeController : Controller { public ActionResult Test() { return new EmptyResult(); } }Make a test.html page with a few img tags that hit that action:
<img src="Home/Test?1" /> <img src="Home/Test?2" /> <img src="Home/Test?3" /> <img src="Home/Test?4" />Run the page & watch the fast load times in firebug:
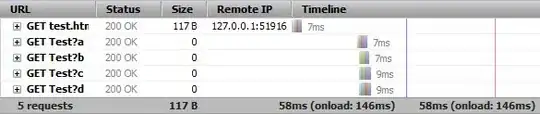
Do one of the follow (both have the same result):
Add an empty Session_Start handler to your Global.asax.cs
public void Session_Start() { }Put something in session
public class HomeController : Controller { public ActionResult Test() { HttpContext.Current.Session["Test"] = 1; return new EmptyResult(); } }
Run the page again & notice the occasional/random delays in the responses.
What I Know So Far
- It happens with MVC 2 & 3 and WebForms
- It happens with any browser (we tried FF, Chrome, IE, Safari)
- It happens regardless of whether the debugger is attached. Also, nothing has to be actually stored in session (see the Session_Start example above).
- It happens with WebDev.exe, IIS Express, & IIS
My Question
How can I use session but avoid these delays? Does anyone know of a fix?
If there's not a fix, I guess we'll have to bypass session & use cookies directly (session uses cookies).