Using rsample::assessment() and rsample::add_resample_id() on a list of rsplit objects should do the trick:
library(sf)
library(rsample)
library(spatialsample)
library(modeldata)
library(tidyr)
library(dplyr)
library(purrr)
library(ggplot2)
data("ames", package = "modeldata")
ames_sf <- sf::st_as_sf(
ames[, c("Street", "Longitude", "Latitude")],
coords = c("Longitude", "Latitude"),
crs = 4326
)
set.seed(123)
# create patial Clustering Cross-Validation folds with kmeans clustering,
# extract assesments from each fold, augment with id
folds_kmeans <- spatial_clustering_cv(ames_sf, v = 15, cluster_function = "kmeans")
clust_fkm <- folds_kmeans$splits %>%
map(~ assessment(.x) %>% add_resample_id(.x)) %>%
bind_rows()
Resulting sf object with 2930 features:
print(clust_fkm, n = 5)
#> Simple feature collection with 2930 features and 2 fields
#> Geometry type: POINT
#> Dimension: XY
#> Bounding box: xmin: -93.69315 ymin: 41.9865 xmax: -93.57743 ymax: 42.06339
#> Geodetic CRS: WGS 84
#> First 5 features:
#> Street id geometry
#> 1 Pave Fold01 POINT (-93.63666 42.05445)
#> 2 Pave Fold01 POINT (-93.63637 42.05027)
#> 3 Pave Fold01 POINT (-93.63937 42.0493)
#> 4 Pave Fold01 POINT (-93.64134 42.0571)
#> 5 Pave Fold01 POINT (-93.64237 42.05306)
Same with hclust, for later comparison:
clust_fhcl <- spatial_clustering_cv(ames_sf, v = 15, cluster_function = "hclust") %>%
pluck("splits") %>%
map(~ assessment(.x) %>% add_resample_id(.x)) %>%
bind_rows()
If it's just for clustering, we can skip spatialsample / rsample and use stats::kmeans() or stats::hclust() with distance matrix ( that's exactly what happens when calling spatialsample::spatial_clustering_cv() ). Here we'll add cluster labels to ames_sf as new columns.
set.seed(123)
# generate distance matrix from sf object to use for clustering
ameas_dist <- ames_sf %>%
st_distance() %>%
as.dist()
# stats::kmeans() clustring
cl_kmeans <- kmeans(ameas_dist, 15)
ames_sf$kmeans_clust <- sprintf("Fold%.2d", cl_kmeans$cluster)
# stats::hclust() clustering
cl_hclust <- hclust(ameas_dist) %>% cutree(k = 15)
ames_sf$hclust <- sprintf("Fold%.2d", cl_hclust)
# ames_sf includes cluster labels from both methods:
print(ames_sf, n = 5)
#> Simple feature collection with 2930 features and 3 fields
#> Geometry type: POINT
#> Dimension: XY
#> Bounding box: xmin: -93.69315 ymin: 41.9865 xmax: -93.57743 ymax: 42.06339
#> Geodetic CRS: WGS 84
#> # A tibble: 2,930 × 4
#> Street geometry kmeans_clust hclust
#> * <fct> <POINT [°]> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 Pave (-93.61975 42.05403) Fold10 Fold01
#> 2 Pave (-93.61976 42.05301) Fold10 Fold01
#> 3 Pave (-93.61939 42.05266) Fold10 Fold01
#> 4 Pave (-93.61732 42.05125) Fold10 Fold01
#> 5 Pave (-93.63893 42.0609) Fold15 Fold02
#> # ℹ 2,925 more rows
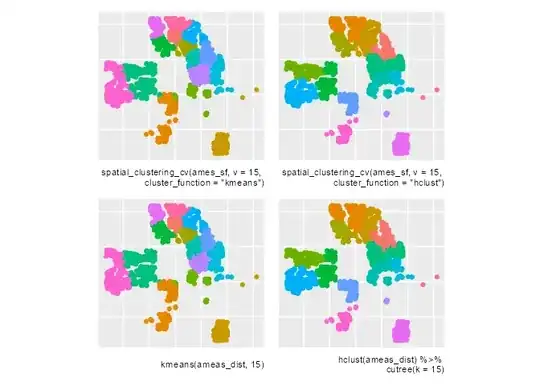
Visual comparison of different methods:
list(
ggplot(clust_fkm) +
labs(caption = 'spatial_clustering_cv(ames_sf, v = 15, \ncluster_function = "kmeans")') +
geom_sf(aes(color = id)),
ggplot(clust_fhcl) +
labs(caption = 'spatial_clustering_cv(ames_sf, v = 15, \ncluster_function = "hclust")') +
geom_sf(aes(color = id)),
ggplot(ames_sf) +
labs(caption = 'kmeans(ameas_dist, 15)') +
geom_sf(aes(color = kmeans_clust)),
ggplot(ames_sf) +
labs(caption = 'hclust(ameas_dist) %>% \ncutree(k = 15)') +
geom_sf(aes(color = hclust))
) %>%
map(~ .x + theme(legend.position = "none",
axis.text = element_blank(),
axis.ticks = element_blank())) %>%
patchwork::wrap_plots()
Created on 2023-07-12 with reprex v2.0.2
