The device ATECC608B is a secure element, and it is designed to protect the private key and prevent it from being extracted. Hence you cannot directly read the private key from the secure element.
You can use the ATECC608B to perform cryptographic operations, such as signing, using the private key stored in the secure element.
And this device provides an API that allows you to sign data using the private key without exposing the key itself.
Steps to follow
Initialize the device ATECC608B and establish a secure connection to it using I2C.
And use the ATECC608B API to sign data. You need to sign the data that Azure IoT Hub requires for authentication.
And pass the signed data or signature using Azure IoT Hub SDK for C as the private key.
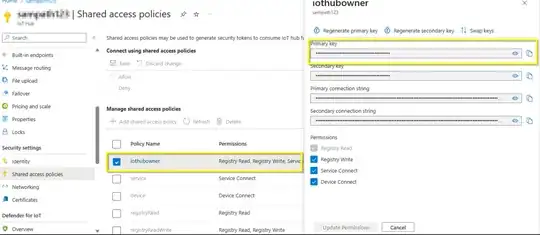
Thanks to shinigami35 for the code reference.
#include <Arduino.h>
#include "ATECCX08A_Arduino/cryptoauthlib.h"
#include "Examples/Configuration/Configuration.h"
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
cfg.iface_type = ATCA_I2C_IFACE;
cfg.devtype = ATECC608A;
cfg.atcai2c.slave_address = 0XC0;
cfg.atcai2c.bus = 1;
cfg.atcai2c.baud = 100000;
cfg.wake_delay = 1500;
cfg.rx_retries = 20;
}
void loop()
{
status = atcab_init(&cfg);
if (status == ATCA_SUCCESS)
{
if (!menu(F("Do you want to write the configuration ?")))
return;
status = write_configuration(&cfg, configuration_example, sizeof(configuration_example));
if (status == ATCA_SUCCESS)
{
if (!menu(F("Do you want to lock the Configuration zone (No more change can be done after that) ?")))
return;
status = lock_zone(&cfg, LOCK_ZONE_CONFIG);
if (status == ATCA_SUCCESS)
{
if (!menu(F("Do you want to write the key in the given slot ?")))
return;
status = write_key_slot(&cfg, KEY_SLOT, example_of_key, sizeof(example_of_key));
if (status == ATCA_SUCCESS)
{
if (!menu(F("Do you want to lock the Data zone (No more change can be done after that) ?")))
return;
status = lock_zone(&cfg, LOCK_ZONE_DATA);
if (status == ATCA_SUCCESS)
{
ATCA_STATUS lock_config = check_lock_zone(&cfg, LOCK_ZONE_CONFIG);
ATCA_STATUS lock_data = check_lock_zone(&cfg, LOCK_ZONE_DATA);
if (lock_config == ATCA_SUCCESS && lock_data == ATCA_SUCCESS)
{
Serial.println("Your chip has been set, you can use it now !");
return;
}
else
{
if (lock_config != ATCA_SUCCESS)
Serial.println("Your config zone has not been locked !");
if (lock_data != ATCA_SUCCESS)
Serial.println("Your data zone has not been locked !");
return;
}
}
else
{
Serial.print(F("Impossible to Lock data | Code Error 0x"));
Serial.println(status, HEX);
return;
}
}
else
{
Serial.print(F("Impossible to Write the key | Code Error 0x"));
Serial.println(status, HEX);
return;
}
}
else
{
Serial.print(F("Impossible to Lock configuration | Code Error 0x"));
Serial.println(status, HEX);
return;
}
}
else
{
Serial.print(F("Impossible to Write configuration | Code Error 0x"));
Serial.println(status, HEX);
return;
}
}
else
{
Serial.print(F("Impossible to Init configuration | Code Error 0x"));
Serial.println(status, HEX);
return;
}
}
Sample code to signIn using C#
Use the Azure IoT Hub Device Provisioning Service (DPS) to provision simulated X.509 device And sign an HTTP request with an HMAC signature for Azure Communication Services using C#
string resrcEndpoint = "resource_Endpoint";
string secret = "resource_AccessKey";
string date = DateTimeOffset.UtcNow.ToString("r", CultureInfo.InvariantCulture);
string host = new Uri(resrcEndpoint).Host;
string path_Query = "/identities?api-version=2021-03-07";
string contnt = JsonConvert.SerializeObject(new { createTokenWithScopes = new[] { "chat" } });
string contHash = ComputeHash(contnt);
string strToSign = $"POST\n{path_Query}\n{date};{host};{contHash}";
string sign = ComputeSign(strToSign, secret);
string auth_Header = $"HMAC-SHA256 SignedHeaders=x-ms-date;host;x-ms-content-sha256&Signature={sign}";
var req_Uri = new Uri($"{resrcEndpoint}{path_Query}");
var reqst = new HttpRequestMessage(HttpMethod.Post, req_Uri)
{
Content = new StringContent(contnt, Encoding.UTF8, "application/json")
};
reqst.Headers.Add("x-ms-date", date);
reqst.Headers.Add("x-ms-content-sha256", contHash);
reqst.Headers.Add("Authorization", auth_Header);
HttpClient httpClnt = new HttpClient { BaseAddress = req_Uri };
var res = await httpClnt.SendAsync(reqst);
var res_Str = await res.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
Console.WriteLine(res_Str);
static string ComputeHash(string contnt)
{
using (var sha256 = SHA256.Create())
{
byte[] hashed_Bytes = sha256.ComputeHash(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(contnt));
return Convert.ToBase64String(hashed_Bytes);
}
}
static string ComputeSign(string stringToSign, string secret)
{
using (var hmacsha256 = new HMACSHA256(Convert.FromBase64String(secret)))
{
var bytes = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(stringToSign);
var hashed_Bytes = hmacsha256.ComputeHash(bytes);
return Convert.ToBase64String(hashed_Bytes);
}
}
The implementation details will depend on the SDK you are using to interact with the ATECC608B and the Azure IoT Hub SDK for C.
For certificate details refer SO link.
For more information refer to the GitHub Link and Azure IoT SDK in ESP-IDF.

