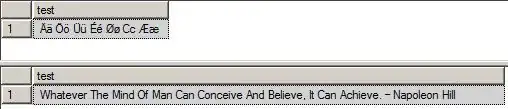
Finally figure out the problem.
Including some answers such as https://stackoverflow.com/a/71154712/9073579, I ended up using a single ScrollView to achieve this functionality.
This approach also introducing the problem that it caused the view to be centered when the height of the inner content was not enough.
Thus, I had to spend additional effort to address this issue. This required additional variables to maintain some state, such as the width of the entire scroll area, and the calculated width of the elements that need to be sticky.
@State private var width: CGFloat? = nil
var body: some View {
ScrollViewReader { proxy in
GeometryReader { geometry in // <-- to get the viewport size
ScrollView([.vertical, .horizontal]) {
ZStack(alignment: .topLeading) { // to place the scroll anchor
VStack(alignment: .leading) {
VStack(alignment: .leading) {
// my headers view here
}
.stickyHorizontal(geometry.size.width, scrollWidth: width)
ForEach(0..<2) { i in
LazyVStack(alignment: .leading, spacing: 0, pinnedViews: .sectionHeaders) {
Section {
... // body table view
} header: {
... // table header
// calculating the width of header (i.e. the width of table)
.background(GeometryReader { geometry in
Color.clear
.onAppear {
width = geometry.size.width
}
.onChange(of: geometry.size.width) { newValue in
width = newValue
}
})
}
}
}
// addtional views (footer)
...
// act as a Spacer(). Stretching the VStack.
Color.clear
.frame(height: geometry.size.height - 40)
}
.frame(width: width)
// scroll destination
Color.clear
.frame(width: 1, height: 1)
.id("topLeading")
}
.onAppear {
// make sure the scroll view appears from top leading.
proxy.scrollTo("topLeading", anchor: .topLeading)
}
}
}
}
}
extension View {
@ViewBuilder
func stickyHorizontal(_ viewPortWidth: CGFloat, scrollWidth: CGFloat?) -> some View {
LazyHStack( spacing: 0, pinnedViews: .sectionHeaders) {
Section {
Color.clear
.frame(width: scrollWidth == nil ? nil : scrollWidth! - viewPortWidth)
} header: {
self
.frame(width: viewPortWidth)
}
}
}
}