I wish to take a concave and complex (containing holes) polygon and extrude it 'vertically' into a polyhedron, purely for visualisation. I begin with a shapely Polygon, like below:
poly = Polygon(
[(0,0), (10,0), (10,10), (5,8), (0,10), (1,7), (0,5), (1,3)],
holes=[
[(2,2),(4,2),(4,4),(2,4)],
[(6,6), (7,6), (6.5,6.5), (7,7), (6,7), (6.2,6.5)]])
which I correctly plot (reorientating the exterior coordinates to be clockwise, and the hole coordinates to be counterclockwise) in matplotlib as:
I then seek to render this polygon extruded out-of-the-page (along z), using PyVista. There are a few hurdles; PyVista doesn't directly support concave (nor complex) input to its PolyData type. So we first create an extrusion of simple (hole-free) concave polygons, as per this discussion.
def extrude_simple_polygon(xy, z0, z1):
# force counter-clockwise ordering, so PyVista interprets polygon correctly
xy = _reorient_coords(xy, clockwise=False)
# remove duplication of first & last vertex
xyz0 = [(x,y,z0) for x,y in xy]
if (xyz0[0] == xyz0[-1]):
xyz0.pop()
# explicitly set edge_source
base_vert = [len(xyz0)] + list(range(len(xyz0)))
base_data = pyvista.PolyData(xyz0, base_vert)
base_mesh = base_data.delaunay_2d(edge_source=base_data)
vol_mesh = base_mesh.extrude((0, 0, z1-z0), capping=True)
# force triangulation, so PyVista allows boolean_difference
return vol_mesh.triangulate()
Observe this works when extruding the outer polygon and each of its internal polygons in-turn:
extrude_simple_polygon(list(poly.exterior.coords), 0, 5).plot()
extrude_simple_polygon(list(poly.interiors[0].coords), 0, 5).plot()
extrude_simple_polygon(list(poly.interiors[1].coords), 0, 5).plot()
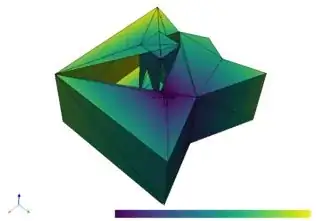
I reasoned that to create an extrusion of the original complex polygon, I could compute the boolean_difference. Alas, the result of
outer_vol = extrude_simple_polygon(list(poly.exterior.coords), 0, 5)
for hole in poly.interiors:
hole_vol = extrude_simple_polygon(list(hole.coords), 0, 5)
outer_vol = outer_vol.boolean_difference(hole_vol)
outer_vol.plot()
is erroneous:
The doc advises to inspect the normals via plot_normals, revealing that all extruded volumes have inward-pointing (or else, unexpected) normals:
The extrude doc mentions nothing of the extruded surface normals nor the original object (in this case, a polygon) orientation.
We could be forgiven for expecting our polygons must be clockwise, so we set clockwise=True in the first line of extrude_simple_polygon and try again. Alas, PolyData now misinterprets our base polygon; calling base_mesh.plot() reveals (what should look like our original blue outer polygon):
with extrusion
- Does PyVista always expect counter-clockwise polygons?
- Why does extrude create volumes with inward-pointing surface normals?
- How can I correct the extruded surface normals?
- Otherwise, how can I make PyVista correctly visualise what should be an incredibly simply-extruded concave complex polygon??