I am trying to create a script that crops parts of a PDF, merges them into a single page, and saves the result to another PDF file. The problem is that when I change the crop box and merge the page, it keeps the cropped data and just hides it. This is a problem because I want to process the output PDF with a parser that extracts the text from the page, rather than using OCR.
Does anyone know how to crop the page and delete the data outside the bounding box?
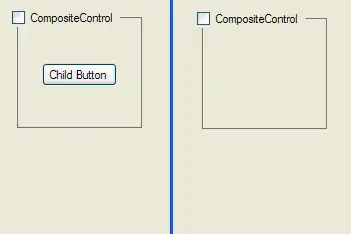
For example: In this PDF file, I want to crop the two blue boxes and merge them into a single page output file. But when I do this and later try to select the text, it still includes the hidden text.
from fitz import Document, Page, Rect
# Define a list of boxes to extract from the input PDF file
# Each box is a dictionary containing the page number and the rectangle coordinates of the box on that page, represented as a Rect object
boxes = [
{
'page_number': 0,
'rect': Rect(0, 54, 595, 189)
},
{
'page_number': 0,
'rect': Rect(0, 317, 595, 459)
}
]
# Calculate the dimensions of the new page as the maximum width and sum of the heights of all the boxes
new_page_rect = Rect(
0,
0,
max([box['rect'].width for box in boxes]) + 1,
sum([box['rect'].height for box in boxes]) + 1
)
# Open the input PDF file and create an output PDF file
with Document(r"lorem_ipsum.pdf") as input_document, Document() as output_document:
# Create a new page in the output document with the calculated width and height
new_page: Page = output_document.new_page(
width=new_page_rect.width,
height=new_page_rect.height
)
# Initialize the y-coordinate for the top of the current box
last_y_coord = 0
# Iterate through each box in the list of boxes
for box in boxes:
# Copy the page from the input document
input_document.copy_page(box['page_number'])
# Get the copied page
page = input_document[-1]
# Set the crop box of the copied page to the rectangle coordinates of the box
page.set_cropbox(box['rect'])
# Calculate the rectangle coordinates for the current box on the new page
rect = Rect(
0,
last_y_coord,
box['rect'].width,
last_y_coord + box['rect'].height,
)
# Update the y-coordinate for the top of the next box to the bottom of the current box
last_y_coord = rect.y1 + 1
# Draw the copied page onto the new page using the calculated rectangle coordinates
new_page.show_pdf_page(rect, input_document, page.number)
# Save the output document as a PDF file
output_document.save(filename=r"output_PyMuPDF.pdf", garbage=3, deflate=True, pretty=True)
I thought the problem could be with the PyMuPDF library, but I tried the equivalent code with PyPDF2 and got the same problem.
import io
import PyPDF2
from PyPDF2 import Transformation
from copy import copy
# Define a list of boxes to extract from the input PDF file
# Each box is a dictionary containing the page number and the rectangle coordinates of the box on that page
boxes = [
{
'page_number': 0,
'rect': (0, 54, 595, 189)
},
{
'page_number': 0,
'rect': (0, 317, 595, 459)
}
]
# Calculate the width of the new page as the maximum width of all the boxes
new_page_width = max([box['rect'][2] - box['rect'][0] for box in boxes]) + 1
# Calculate the height of the new page as the sum of the heights of all the boxes
new_page_height = sum([box['rect'][3] - box['rect'][1] for box in boxes]) + 1
# Open the input PDF file and create an output PDF file
with open(r"lorem_ipsum.pdf", "rb") as input_file, open(r"output_PyPDF2.pdf", "wb") as output_file:
# Create a PDF reader object to read the input PDF file
reader = PyPDF2.PdfFileReader(input_file)
# Create a PDF writer object to write the output PDF file
writer = PyPDF2.PdfFileWriter()
# Clone the input PDF file using the writer object, so that we can modify it without changing the original file
temp_writer = PyPDF2.PdfFileWriter()
temp_writer.clone_document_from_reader(reader=reader)
# Create a blank page with the calculated width and height using the PyPDF2 PageObject class
new_page = PyPDF2.PageObject.create_blank_page(
pdf=None,
width=new_page_width,
height=new_page_height
)
# Initialize the y-coordinate for the top of the new page
last_y_coord = new_page_height
# Iterate through each box in the list of boxes
for box in boxes:
# Extract the corresponding page from the reader object
page = copy(reader.getPage(box['page_number']))
# Get the height of the page
page_height = page.mediabox.upper_right[1]
# Calculate the coordinates of the top-left and bottom-right corners of the box
x0 = box['rect'][0]
y0 = page_height - box['rect'][3]
x1 = box['rect'][2]
y1 = page_height - box['rect'][1]
# Calculate the translation transformation to apply to the page
# The transformation moves the page horizontally by the distance from the left edge of the page to the left edge of the box
# and moves the page vertically by the distance from the top of the current box to the bottom of the last added page
tx = -x0
ty = last_y_coord - y1
# Create a transformation object using the PyPDF2 Transformation class
transformation = Transformation().translate(
tx=tx,
ty=ty
)
# Apply the transformation to the page
page.add_transformation(transformation)
# Update the page's cropbox to reflect the transformation
page.cropbox.lower_left = (x0, y0 + ty)
page.cropbox.upper_right = (x1, y1 + ty)
# Merge the transformed page onto the new page
new_page.merge_page(page)
# Update the y-coordinate for the top of the next box to the top of the current box
last_y_coord -= (y1 - y0 + 1)
# After all boxes have been processed, add the new page to the writer object
writer.addPage(new_page)
# Write the output PDF file using the writer object
writer.write(output_file)