My objective is to parallelise a one-dimensional integral. I have looked around, and I would say that I could do that in two ways: i) implementing OpenMP with ODEINT, boost library integrate_adapative function (see https://www.boost.org/doc/libs/1_56_0/libs/numeric/odeint/doc/html/boost_numeric_odeint/tutorial/parallel_computation_with_openmp_and_mpi.html).; ii) implementing OpenMP with GSL monte carlo integration (as in here: Internal compiler error with nested functions in OpenMP parallel regions).
My problem is that I cannot really understand what they did in both links I provided.
I was wondering whether someone has experience with that, and may point out how I could implement both approaches on my case. Is it OpenMP with boost faster or GSL and OpenMP implementation?
PDFfunction represents the probability density function that is used within the integrand function. PDFfunction is equivalent to 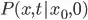 , and in LateX is expressed as:
, and in LateX is expressed as:

And this is how I code it:
double PDFfunction(double invL, int t, double invtau, double x0, double x, int n) {
const double c = M_PI * (M_PI/4) * ((2 * t) * invtau);
double res = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++n){
res += exp(-1 * (i * i) * c) * cos((i * M_PI * x) * invL) * cos((i * M_PI * x0) * invL);
}
return invL + ((2 * invL) * res);
}
Composite_at_t is a function that makes use of the PDFfunction to compute pbA and pbB. Composite_at_t is equivalent to 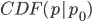 , where
, where 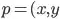 ) and
) and 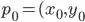 ).
).
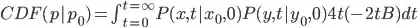
double Composite_at_t(double t, double B, double x0, double xt_pos, double y0, double yt_pos, double invLtot, double invtau, int n_lim) {
double pbA = PDFfunction(invLtot, t, invtau, x0, xt_pos, n_lim);
double pbB = PDFfunction(invLtot, t, invtau, y0, yt_pos, n_lim);
double b1 = 2 * (2 * t) * exp(-2 * t * B);
return pbA * pbB * b1;
}
Composite_at_tCLASS is a Func class which computes a first integral over variable t.
class Composite_at_tCLASS: public Func{
private:
double B;
double x0;
double xt_pos;
double y0;
double yt_pos;
double invLtot;
double invtau;
int n_lim;
public:
Composite_at_tCLASS(double B_, double x0_, double xt_pos_, double y0_, double yt_pos_, double invLtot_, double invtau_, int n_lim_) : B(B_), x0(x0_), xt_pos(xt_pos_), y0(y0_), yt_pos(yt_pos_), invLtot(invLtot_), invtau(invtau_), n_lim(n_lim_) {}
double operator()(const double& t) const{
return Composite_at_t(t, B, x0, xt_pos, y0, yt_pos, invLtot, invtau, n_lim);
}
};
integrate_CompositeCLASS is the actual function that uses the class Composite_at_tCLASS and perform the integral over t, between 0 and time_lim.
double integrate_CompositeCLASS(double B, double x0, double xt_pos, double y0, double yt_pos, double invLtot, double invtau, int n_lim, double time_lim){
Composite_at_tCLASS f(B, x0, xt_pos, y0, yt_pos, invLtot, invtau, n_lim);
double err_est;
int err_code;
double res = integrate(f, 0, time_lim, err_est, err_code);
return res;
}
For the numerical integration using the GSL library I would use the following code:
struct my_f_params { double B; double x0; double xt_pos; double y0; double yt_pos; double invtau; int n_lim; double invLtot;};
double g(double *k, size_t dim, void *p){
struct my_f_params * fp = (struct my_f_params *)p;
return Composite_at_t(k[0],fp->B, fp->x0, fp->xt_pos, fp->y0, fp->yt_pos, fp->invLtot, fp->invtau, fp->n_lim);
}
And this is the actual object that perform the GSL integral:
double integrate_integral(const double& invtau, const int& n_lim, const double& invLtot,
const double& x0, const double& xt_pos, const double& y0, const double& yt_pos, const double& time_lim){
double res, err;
double xl[1] = {0};
double xu[1] = {time_lim};
const gsl_rng_type *T;
gsl_rng *r;
gsl_monte_function G;
struct my_f_params params = { B, x0, xt_pos, y0, yt_pos, invtau, n_lim, invLtot};
G.f = &g;
G.dim = 1;
G.params = ¶ms;
size_t calls = 10000;
gsl_rng_env_setup ();
T = gsl_rng_default;
r = gsl_rng_alloc (T);
gsl_monte_vegas_state *s = gsl_monte_vegas_alloc (1);
gsl_monte_vegas_integrate (&G, xl, xu, 1, 10000, r, s,
&res, &err);
do
{
gsl_monte_vegas_integrate (&G, xl, xu, 1, calls/5, r, s,
&res, &err);
}
while (fabs (gsl_monte_vegas_chisq (s) - 1.0) > 0.5);
gsl_monte_vegas_free (s);
gsl_rng_free (r);
return res;
}