There are syntax errors in the function shown in the question so we used the one in the Note at the end.
If that function is a density and you want to minimize the corresponding negative log likelihood then trying a few different starting values these seem to result in convergence.
(For the x given in a comment below the question list(a = 1, b = 1, alpha = 575, vartheta = 0.01) seems to work as starting values.)
NLL <- function(par) -sum(log(EMHL(par[1], par[2], par[3], par[4])))
st <- list(a = 1, b = 1, alpha = 525, vartheta = .2)
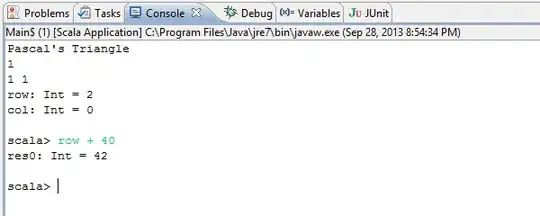
res <- optim(st, NLL); res
giving:
$par
a b alpha vartheta
8.845296e-01 1.211526e+00 5.315759e+02 1.326975e-03
$value
[1] -10904.36
$counts
function gradient
327 NA
$convergence
[1] 0
$message
NULL
L-BFGS-B
Using L-BFGS-B with the function above results in problems but an answer can be obtained if we constrain the parameters. For example, this converges with all the constraints being active, i.e. the solution is on the boundary of the feasible region. Note that tests and p values derived from estimates on a boundary may not be valid.
optim(c(1, 1, 1, 1), NLL, method = "L-BFGS-B", lower = 0.01, upper = 2)
Other densities
Another possibility is to use a different distribution. The Cullen & Frey diagram produced by descdist suggests that the gamma distribution may be close
library(fitdistrplus)
descdist(x)
(continued after graph)
or we could try the generalized gamma (dgengamma) in the flexsurv package.
library(bbmle)
library(flexsurv)
NLLgeng <- function(mu, sigma, Q) -sum(dgengamma(x, mu, sigma, Q, log = TRUE))
m <- mle2(NLLgeng, list(mu = 1, sigma = 1, Q = 1), optimizer = "nlminb")
summary(m)
library(fitdistrplus)
fit <- fitdist(x, "gengamma", start = list(mu = 1, sigma = 1, Q = 1))
summary(fit)
plot(fit)
Note
EMHL<-function(a,b,alpha,vartheta) {
2 * a * b * alpha * vartheta *
(x^(vartheta-1))* exp(-x^vartheta) *((1-exp(-x^vartheta))^(a-1)) *
((1 - (1 -( 1 - exp(-x^vartheta))^a)^b)^(alpha-1)) *
(1- (1 - exp(-x^vartheta))^a )^(-b*(alpha+1))
}
x<- c(1.1, 1.4, 1.3, 1.7,1.9, 1.8, 1.6, 2.2, 1.7, 2.7, 4.1, 1.8,
1.5, 1.2, 1.4, 3, 1.7, 2.3, 1.6, 2.0)

