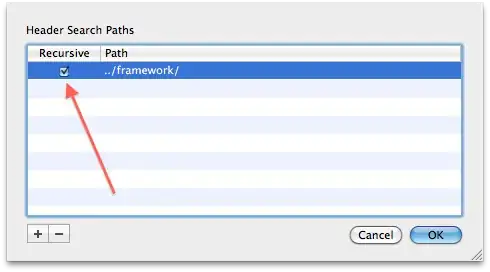
I have been struggling to solve the following question using Recessive Backtracking in C++. The problem is that it does not backtrack. I tracked my algorithm manually on a paper and it works on the paper. So problem is I don't know how to implement that in C++. Any help will be appreciated.
Question:
Given a 2-dimensional grid representing elevations of a map, determine the lowest and highest points and whether there is a path between them that never goes down.
Input
Your program will receive the following command line arguments:
<fname> File name for the 2-dimensional map
<M> Number of rows
<N> Number of columns
Output
Your program should write 5 values to the standard output: Lr Lc Hr Hc YESNO where Lr Lc are the row and column of the lowest point in the grid, Hr Hc are the row and column of the highest point in the grid, and YESNO is the word: yes if there is a path from the lowest point to the highest point that never goes down and no if there is no such path. Specifically, the path starts at the lowest point and can only go from a point to one of its 4-neighbors (left, right, up, or down) that does NOT have a lower elevation than the point. Input will be such that there is a unique solution.
The problem is with the "path" function.
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include<string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include<sstream>
// using namespace std;
void ReadFile(std::string fname, std::vector<std::vector<int>> *const vec_2d);
// What about min? row and col are initially the min, but then get updated
void min_max(std::vector<std::vector<int>> *const vec_2d,
std::vector<int> &vec_1d,
int num_rows,
int num_cols,
int &row,
int &col,
int &idx_i_max,
int &idx_j_max,
int &cur_val); //grid is vec_2d??????
int path(std::vector<int> vec_1d,
int row,
int col,
int num_rows,
int num_cols,
int idx_i_max,
int idx_j_max,
int &cur_val); // bool *visited is a pointer type bool which could be a 2-d array??
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
std::vector<std::vector<int>> vec_2d;
std::vector<int> vec_1d;
// declare variables
int num_rows, num_cols, row, col, idx_i_max, idx_j_max, cur_val;
std::string fname;
// get .txt file containing the grid
fname = argv[1]; //string of file name
num_rows = atoi(argv[2]); // convert argument strings to integers
num_cols = atoi(argv[3]);
// bool visited[100][100];
//2D vector initialized with user defined size
// std::vector<std::vector<int>> visited(num_rows, std::vector<int>(num_cols));
ReadFile(fname, &vec_2d); //reading the .txt file and assigning to vec_2d
min_max(&vec_2d,
vec_1d,
num_rows,
num_cols,
row,
col,
idx_i_max,
idx_j_max,
cur_val);
path(vec_1d, row, col, num_rows, num_cols, idx_i_max, idx_j_max, cur_val);
}
void ReadFile(std::string fname, std::vector<std::vector<int>> *const vec_2d)
{ //it is a pointer to a vector,therefore, after end of func, it will still exist // Create the input filestream - opens the file & prepares it for reading
std::ifstream file(fname);
std::string str; // Temporary string to hold a single line of the file
while (std::getline(file, str))
{ // Reads all lines in the file, 1 at at time
std::vector<int> new_row; // Creates a temporary vector to represent one row
std::istringstream ss(str); // Converts our string into a stringstream
int token; // Temp int to store a converted value from a line
while (ss >> token)
{ // Reads all values from the stringstream (current row), converts to int
new_row.push_back(token); // Adds the converted value to the row
}
vec_2d->push_back(new_row); // Pushes our constructed vector of ints to the 2D vector
}
}
void min_max(std::vector<std::vector<int>> *const vec_2d,
std::vector<int> &vec_1d,
int num_rows,
int num_cols,
int &row,
int &col,
int &idx_i_max,
int &idx_j_max,
int &cur_val)
{ //I dont need any argument for this func
//Converting 2-d vec to 1-d to find loc of min and max
for (int i = 0; i < (*vec_2d).size(); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < (*vec_2d)[i].size(); j++)
{
vec_1d.push_back((*vec_2d)[i][j]);
}
}
// finding the max and min values in the grid vector and save thier index (max_idx and min_idx)
int max_idx, min_idx; // Initialize two int for index of max and min values
//
int maxElementIndex = std::max_element(vec_1d.begin(), vec_1d.end())
- vec_1d.begin(); //max elem index //I need to convert 2d to 1d vector to use this func
int minElementIndex = std::min_element(vec_1d.begin(), vec_1d.end())
- vec_1d.begin(); //min elem index
//convert 1-d vec idx to 2-d vec idx
idx_i_max = (maxElementIndex / num_cols) + 1; //actual idx + 1
idx_j_max = (maxElementIndex % num_cols) + 1; //actual idx + 1
int idx_i_min = (minElementIndex / num_cols) + 1; //actual idx + 1
int idx_j_min = (minElementIndex % num_cols) + 1; //actual idx + 1
// The initial current value is the minimum
cur_val = *std::min_element(vec_1d.begin(), vec_1d.end());
//loc of min will be our start point as below
row = idx_i_min; //actual idx + 1
col = idx_j_min; //actual idx + 1
// print i and j idx of min and max respectively (with a space after each)
std::cout << idx_i_min << " ";
std::cout << idx_j_min << " ";
std::cout << idx_i_max << " ";
std::cout << idx_j_max << " "; //This prints are working fine
// A recursive backtracking function to go over all cells. base case is when all directions are impossible, then retuen 0
}
//row and col will be changed in every recursion. should they be const???
int path(std::vector<int> vec_1d,
int row,
int col,
int num_rows,
int num_cols,
int idx_i_max,
int idx_j_max,
int &cur_val)
{
// std::cout<<"test"<<std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl << row << " " << col << std::endl; // it atops at the second cell
// std::cout<<cur_val<<std::endl;//it prints the start point twice
// if the evaluating neighbor cell is equal to max value
if (row == idx_i_max && col == idx_j_max)
{ //base case
std::cout << "yes";
return 1;
}
else
{
cur_val = vec_1d[((row - 1) * num_cols) + (col - 1)]; //updating the current value
//Checking the north neighbor (COND1)
if (row - 1 > 0
&& vec_1d[((row - 1 - 1) * num_cols) + (col - 1)] >= cur_val)
{ //if the north cell is -1
vec_1d[((row - 1) * num_cols) + (col - 1)] = -1; // making the current cell as visited
path(vec_1d,
row - 1,
col,
num_rows,
num_cols,
idx_i_max,
idx_j_max,
cur_val);
return 1;
}
//Checking the south neighbor(COND2)
if (row + 1 <= num_rows
&& vec_1d[((row + 1 - 1) * num_cols) + (col - 1)] >= cur_val)
{
vec_1d[((row - 1) * num_cols) + (col - 1)] = -1;
path(vec_1d,
row + 1,
col,
num_rows,
num_cols,
idx_i_max,
idx_j_max,
cur_val);
return 1;
}
//Checking the west neighbor(COND3)
if (col - 1 > 0
&& vec_1d[((row - 1) * num_cols) + (col - 1 - 1)] >= cur_val)
{
vec_1d[((row - 1) * num_cols) + (col - 1)] = -1;
path(vec_1d,
row,
col - 1,
num_rows,
num_cols,
idx_i_max,
idx_j_max,
cur_val);
return 1;
}
//Checking the east neighbor(COND4)
if (col + 1 <= num_cols
&& vec_1d[((row - 1) * num_cols) + (col + 1 - 1)] >= cur_val)
{
vec_1d[((row - 1) * num_cols) + (col - 1)] = -1;
path(vec_1d,
row,
col + 1,
num_rows,
num_cols,
idx_i_max,
idx_j_max,
cur_val);
return 1;
}
// return 0;
}
// FORGET ABOUT PRINTING YES/NO. FOCUS ON THE PRINT OF CURRENT CELL
// if(path){
// std::cout<<"yes";
// }
// else{
// std::cout<<"no";
// }
}