Firstly, because the code I am using is big so here is the link to the code.
I have this function that runs other functions if a specific input is given:
allowed_commands = ['help', 'joblist', 'job', 'jobresign', 'work', 'bal', 'balance', 'dep', 'deposit', 'with', 'withdraw', 'fish', 'hunt', 'shop', 'buy', 'sell', 'hunt', 'fish', 'multiply']
def gamePlay():
while True:
command = input(f"{bright_green}Command (type [help] to see list of all commands):\n>> ")
while command in allowed_commands:
# <-- Display Rules -->
if command == 'help':
rules()
break
# <-- Display Jobs -->
elif command == 'joblist':
joblist_function()
break
# <-- Get Jobs -->
elif command == 'job' and working == False:
job_funtion()
break
elif command == 'job' and working == True:
print(f"\n{red}You are already doing a job. You can't work on two jobs,that is dumb...\n")
break
# <-- Resign Job -->
elif command == 'jobresign':
job_resign()
break
# <-- Work -->
elif command == 'work' and working == True:
work()
break
elif command == "work" and working == False:
print(f"{red}\nLOL, you don't have a job, how you gonna work?\n")
break
# <-- Deposit -->
elif command == 'dep' or command == 'deposit' and deposit_allowed != deposited:
dep_money()
break
elif command == 'dep' or command == 'deposit' and deposit_allowed == deposited:
print("You have a full bank kiddo...")
break
# <-- Balance -->
elif command == 'bal' or command == 'balance':
display_balance()
break
# <-- Withdraw -->
elif command == 'with' or command == 'withdraw' and deposited != 0:
withdraw_money()
break
elif command == 'with' or command == 'withdraw' and deposited == 0:
print(f"{red}\nNo money deposited. What are you even trying to wothdraw LOL?\n")
break
elif command == 'shop':
shop()
break
elif command == 'beg':
beg()
break
def beg():
global money
random_number2 = random.choice([0, 1, 2])
random_money = random.choice(range(100, 500))
if random_number2 == 1:
print("Ewwww beggar. No stonks for u")
if random_number2 == 2:
print(f"Mr.beggar, you can have ⏣ {random_money}.")
money += random_money
But the tooltip on the green line under the function says "Cyclomatic complexity too high: 17 (threshold 15)".
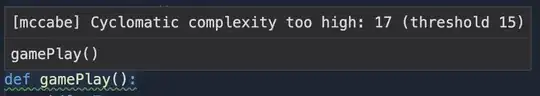
Normally, this would work in my code even though the complexity was up to 30. But the code after the last elif is not working. Even when I input 'beg', the function doesn’t run:
Command (type [help] to see list of all commands):
>> beg
Command (type [help] to see list of all commands):
>> beg
Command (type [help] to see list of all commands):
>>
Why is this happening and how can I solve it?