I tried to solve a 2D optimal lunar soft landing problem by GEKKO. I assume that the moon is not rotating. The spacecraft is supposed to land softly on the surface of the moon, i.e. the final vertical velocity v and the final horizontal velocity u should be zero, the final height r should be the radius of the moon.
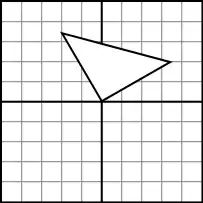
The problem can be illustrated as follows:
The state and control variables as well as equations are listed as follows (control variables are thrust force F and attitude angle φ):
I constructed the fuel optimal problem as follows (control variable φ is written as f):
from gekko import GEKKO
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import time
import os
r0=1753000
v0=1675
time_start = time.time()
model = GEKKO()
nt = 501
model.time = np.linspace(0,1,nt)
# optimize final time
tf = model.FV(value=1.0,lb=0.1,ub=1000.0)
tf.STATUS = 1
# controls
F = model.MV(value=0,lb=0,ub=2000)
F.STATUS = 1
f = model.MV(value=-0.5*np.pi,lb=-0.5*np.pi,ub=0.5*np.pi)
f.STATUS = 1
# state variables
r = model.Var(value=r0,lb=1738000) # height
s = model.Var(value=0) # tru anomaly
v = model.Var(value=0) # vertical velocity
u = model.Var(value=v0) # horizional velocity
m = model.Var(value=600,lb=0,ub=600) # mass
# constants
mu = 4.90275*10**(12) # lunar gravitational constant
Isp = 300*9.8 # specific impulse
# Equations
model.Equation( r.dt() == tf * v )
model.Equation( s.dt() == tf * u/r )
model.Equation( v.dt() == tf * (F/m*model.cos(f)-mu/(r**2)+u**2/r) )
model.Equation( u.dt() == tf * (F/m*model.sin(f)-u*v/r) )
model.Equation( m.dt() == tf * (-F/Isp) )
# terminal constraints
_finalMask = np.zeros(nt)
_finalMask[-1] = 1.0
finalMask = model.Param(value=_finalMask)
model.Equation(v*finalMask>=0)
model.Equation(v*finalMask<=0.5)
model.fix_final(r,val=1738000)
model.fix_final(u,val=0)
model.Obj(-m*finalMask) # Objective function to be minimized
model.options.IMODE = 6
model.solver_options = ['max_iter 5000']
model.solve() # solve
time_end=time.time()
print('Calculation Time: ',time_end-time_start)
# scaled time
print('Landing Time: ' + str(tf.value[0]))
tm = np.linspace(0,tf.value[0],nt)
finaltime = tm[-1]
# PLOT
fig = plt.figure(1)
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(2, 3, 1)
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(2, 3, 2)
ax3 = fig.add_subplot(2, 3, 3)
ax4 = fig.add_subplot(2, 3, 4)
ax5 = fig.add_subplot(2, 3, 5)
ax6 = fig.add_subplot(2, 3, 6)
ax1.plot(tm,r.value,'k-',label=r'$r$')
ax1.set_xlabel('Time')
ax1.set_ylabel('r')
ax1.set_xlim(0,finaltime)
ax2.plot(tm,v.value,'b-',label=r'$v$')
ax2.set_xlabel('Time')
ax2.set_ylabel('v')
ax2.set_xlim(0,finaltime)
ax3.plot(tm,u.value,'g-',label=r'$w$')
ax3.set_xlabel('Time')
ax3.set_ylabel('u')
ax3.set_xlim(0,finaltime)
ax4.plot(tm,m.value,'y-',label=r'$m$')
ax4.set_xlabel('Time')
ax4.set_ylabel('m')
ax4.set_xlim(0,finaltime)
ax5.plot(tm,f.value,'c-',label=r'$f$')
ax5.set_xlabel('Time')
ax5.set_ylabel('f')
ax5.set_xlim(0,finaltime)
ax6.plot(tm,F.value,'r-',label=r'$F$')
ax6.set_xlabel('Time')
ax6.set_ylabel('F')
ax6.set_xlim(0,finaltime)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
It can found a solution very similar to other's research.
but there is a sharp turn in f. It is unacceptable because the angle φ should be continuously changed .
Also, I tried to scale the function
scale = 1e-6
model.Equation( r.dt() == tf * v )
model.Equation( r*s.dt()*scale == tf * u*scale )
model.Equation( m*(r**2)*v.dt()*scale**2 == tf * ((r**2)*F*model.cos(f)-mu*m+(u**2)*r*m)*(scale**2) )
model.Equation( m*r*u.dt()*scale == tf * (F*r*model.sin(f)-u*v*m)*scale )
model.Equation( Isp*m.dt() == tf * (-F) )
but failed with
Solution Not Found
EXIT: Converged to a point of local infeasibility. Problem may be infeasible.
In order to get a smooth f, I changed the second control variable to angular acceleration a, and the state equation became
the code became:
from gekko import GEKKO
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import time
import os
r0=1753000
v0=1675
time_start = time.time()
model = GEKKO() # remote=False
nt = 501
model.time = np.linspace(0,1,nt)
tf = model.FV(value=1.0,lb=0.1,ub=1000.0)
tf.STATUS = 1
# controls
F = model.MV(value=0,lb=0,ub=2000)
F.STATUS = 1
a = model.MV(value=0,lb=-0.5*np.pi/180,ub=0.5*np.pi/180)
a.STATUS = 1
# state variables
r = model.Var(value=r0,lb=1738000) # height
s = model.Var(value=0) # tru anomaly
v = model.Var(value=0) # vertical velocity
u = model.Var(value=v0) # horizional velocity
f = model.Var(value=-0.5*np.pi) # angle
w = model.Var(value=0, lb=-10*np.pi/180,ub=10*np.pi/180) # angular velocity
m = model.Var(value=600,lb=0,ub=600) # mass
# constants
mu = 4.90275*10**(12) # lunar gravitational constant
Isp = 300*9.8 # specific impulse
# Equations
model.Equation( r.dt() == tf * v )
model.Equation( s.dt() == tf * u/r )
model.Equation( v.dt() == tf * (F/m*model.cos(f)-mu/(r**2)+u**2/r) )
model.Equation( u.dt() == tf * (F/m*model.sin(f)-u*v/r) )
model.Equation( f.dt() == tf * (w - u/r) ) # ---newly added
model.Equation( w.dt() == tf * a ) # ---newly added
model.Equation( m.dt() == tf * (-F/Isp) )
# terminal constraints
_finalMask = np.zeros(nt)
_finalMask[-1] = 1.0
finalMask = model.Param(value=_finalMask)
model.Equation(v*finalMask>=0)
model.Equation(v*finalMask<=0.5)
model.Equation(f*finalMask>=-5*np.pi/180) # ***newly added
model.Equation(f*finalMask<=5*np.pi/180) # ***newly added
model.fix_final(r,val=1738000)
model.fix_final(u,val=0)
model.Obj(-m*finalMask) # Objective function to be minimized
model.options.IMODE = 6
model.solver_options = ['max_iter 99999']
model.solve() # solve
time_end=time.time()
print('Calculation Time: ',time_end-time_start)
# scaled time
print('Landing Time: ' + str(tf.value[0]))
tm = np.linspace(0,tf.value[0],nt)
finaltime = tm[-1]
# PLOT
fig = plt.figure(1)
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(2, 4, 1)
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(2, 4, 2)
ax3 = fig.add_subplot(2, 4, 3)
ax4 = fig.add_subplot(2, 4, 4)
ax5 = fig.add_subplot(2, 4, 5)
ax6 = fig.add_subplot(2, 4, 6)
ax7 = fig.add_subplot(2, 4, 7)
ax8 = fig.add_subplot(2, 4, 8)
ax1.plot(tm,r.value,'k-',label=r'$r$')
ax1.set_xlabel('Time')
ax1.set_ylabel('r')
ax1.set_xlim(0,finaltime)
ax2.plot(tm,v.value,'b-',label=r'$v$')
ax2.set_xlabel('Time')
ax2.set_ylabel('v')
ax2.set_xlim(0,finaltime)
ax3.plot(tm,u.value,'g-',label=r'$u$')
ax3.set_xlabel('Time')
ax3.set_ylabel('u')
ax3.set_xlim(0,finaltime)
ax4.plot(tm,m.value,'y-',label=r'$m$')
ax4.set_xlabel('Time')
ax4.set_ylabel('m')
ax4.set_xlim(0,finaltime)
ax5.plot(tm,F.value,'r-',label=r'$F$')
ax5.set_xlabel('Time')
ax5.set_ylabel('F')
ax5.set_xlim(0,finaltime)
ax6.plot(tm,f.value,'k-',label=r'$f$')
ax6.set_xlabel('Time')
ax6.set_ylabel('f')
ax6.set_xlim(0,finaltime)
ax7.plot(tm,w.value,'b-',label=r'$w$')
ax7.set_xlabel('Time')
ax7.set_ylabel('w')
ax7.set_xlim(0,finaltime)
ax8.plot(tm,a.value,'r-',label=r'$a$')
ax8.set_xlabel('Time')
ax8.set_ylabel('a')
ax8.set_xlim(0,finaltime)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
however, I've ran the code for many hours but didn't get a solution or result. More specifically, it stops at certain iterations:
I tried to use soft terminal constraints but also failed to get any result:
model.Equation(r*finalMask>=1738000)
model.Equation(r*finalMask<=1738001)
model.Equation(v*finalMask>=0)
model.Equation(v*finalMask<=0.5)
model.Equation(u*finalMask>=-0.5)
model.Equation(u*finalMask<=0.5)
model.Equation(f*finalMask>=-5*np.pi/180)
model.Equation(f*finalMask<=5*np.pi/180)