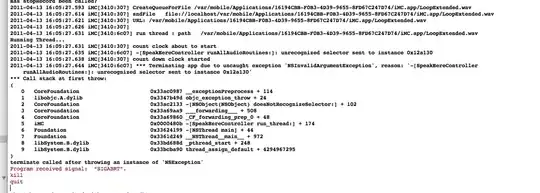
I have two polygons. I want to combine them into one polygon such that it includes the exterior points only without any holes.
How can I do that? Code with little explanation would be very helpful. Thank you.
See the picture for better understanding.
Asked
Active
Viewed 1,508 times
2
sehe
- 374,641
- 47
- 450
- 633
Masum Bhuiyan
- 47
- 8
1 Answers
3
I think you can just use the union_ algorithm
polygon a, b;
bg::read_wkt("POLYGON((0 0, 5 5, 9 0, 0 0))", a);
bg::read_wkt("POLYGON((5 1, 10 5, 10 -2, 5 1))", b);
std::string reason;
std::cout << std::boolalpha;
std::cout << bg::is_valid(a, reason) << " (" << reason << ")\n";
std::cout << bg::is_valid(b, reason) << " (" << reason << ")\n";
multi_polygon ab;
bg::union_(a, b, ab);
write_svg("union.svg", a, b, ab);
Creates
Trouble
Of course, replacing with your second example
bg::read_wkt("POLYGON((0 0, 0 5, 3 5, 1 2, 3 0, 0 0))", a);
bg::read_wkt("POLYGON((5 0, 10 5, 14 0, 5 0))", b);
Just results in the polygons separately. This is the correct answer:
It's correct because there is no overlap. Slapping together the polygons by force as you did is
- arbitrary (you could join them by different artifical lines)
- invalid (the resulting polygon is self intersecting)
See e.g.
for (auto wkt : {
"POLYGON((0 0, 0 5, 3 5, 1 2, 3 0, 5 0, 10 5, 14 0, 5 0, 3 0, 0 0))",
"POLYGON((0 0, 0 5, 3 5, 1 2, 3 0, 5 0, 10 5, 14 0, 5 0, 0 0))",
"POLYGON((0 0, 0 5, 3 5, 1 2, 3 0, 5 0, 10 5, 14 0, 0 0))",
}) {
polygon invalid;
bg::read_wkt(wkt, invalid);
std::cout << bg::is_valid(invalid, reason) << " (" << reason << ")\n";
}
Prints
false (Geometry has invalid self-intersections. A self-intersection point was found at (3, 0); method: t; operations: x/i; segment IDs {source, multi, ring, segment}: {0, -1, -1, 3}/{0, -1, -1, 8})
false (Geometry has invalid self-intersections. A self-intersection point was found at (3, 0); method: m; operations: x/i; segment IDs {source, multi, ring, segment}: {0, -1, -1, 3}/{0, -1, -1, 8})
false (Geometry has invalid self-intersections. A self-intersection point was found at (3, 0); method: m; operations: x/i; segment IDs {source, multi, ring, segment}: {0, -1, -1, 3}/{0, -1, -1, 7})
Forcing The Issue
Doesn't work, e.g.:
polygon force_combine;
bg::append(force_combine, a.outer());
bg::append(force_combine, b.outer());
force_fix(force_combine);
With
template <typename G> void force_fix(G& g) {
G previous;
std::string reason;
do {
if (bg::is_valid(g, reason))
return;
std::cout << "Invalid: " << reason << "\n";
previous = g;
bg::correct(g);
} while (!bg::equals(previous, g));
std::cout << "Warning: could not force_fix\n";
}
Prints
Invalid: Geometry is defined as closed but is open
Warning: could not force_fix
Full Demo Code
#include <boost/geometry/geometry.hpp>
#include <boost/geometry/geometries/point_xy.hpp>
#include <boost/geometry/geometries/polygon.hpp>
#include <boost/geometry/geometries/multi_polygon.hpp>
#include <iostream>
namespace bg = boost::geometry;
namespace bgm = bg::model;
using point = bgm::d2::point_xy<double>;
using polygon = bgm::polygon<point>;
using multi_polygon = bgm::multi_polygon<polygon>;
template <typename G>
void write_svg(std::string fname, polygon const& a, polygon const& b, G const& g);
template <typename G>
void force_fix(G& g);
struct { std::string a,b; } const examples[] = {
{ "POLYGON((0 0, 5 5, 9 0, 0 0))",
"POLYGON((5 1, 10 5, 10 -2, 5 1))" },
{ "POLYGON((0 0, 0 5, 3 5, 1 2, 3 0, 0 0))",
"POLYGON((5 0, 10 5, 14 0, 5 0))" } };
int main() {
int n = 0;
for (auto example : examples) {
++n;
polygon a, b;
bg::read_wkt(example.a, a);
bg::read_wkt(example.b, b);
force_fix(a); // input sanitation if needed
force_fix(b);
multi_polygon ab;
bg::union_(a, b, ab);
write_svg("example" + std::to_string(n) + ".svg", a, b, ab);
std::cout << "Example " << n << " is compound? " << (ab.size() > 1) << "\n";
}
}
#include <fstream>
template <typename G>
void write_svg(std::string fname, polygon const& a, polygon const& b, G const& g) {
std::ofstream ofs(fname);
bg::svg_mapper<point> mapper(ofs, 400, 400);
mapper.add(g);
mapper.map(g, "fill-opacity:0.1;fill:rgb(100,0,0);stroke:rgb(200,0,0);stroke-width:2", 5);
mapper.add(a);
mapper.map(a, "fill-opacity:0.01;fill:rgb(0,100,0);stroke:rgb(0,200,0);stroke-width:1;stroke-dasharray:4", 5);
mapper.add(b);
mapper.map(b, "fill-opacity:0.01;fill:rgb(0,0,100);stroke:rgb(0,0,200);stroke-width:1;stroke-dasharray:4", 5);
}
template <typename G> void force_fix(G& g) {
G previous;
std::string reason;
do {
if (bg::is_valid(g, reason))
return;
std::cout << "Invalid: " << reason << "\n";
previous = g;
bg::correct(g);
} while (!bg::equals(previous, g));
std::cout << "Warning: could not force_fix\n";
}
Prints
Example 1 is compound? 0
Example 2 is compound? 1
sehe
- 374,641
- 47
- 450
- 633