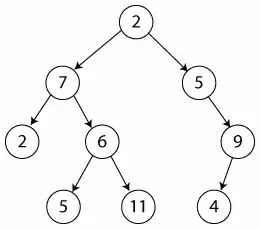
If we are able to fetch the next element at same level, we are done. As per our prior knowledge, we can access these element using breadth first traversal.
Now only problem is how to check if we are at last element at any level. For this reason, we should be appending a delimiter (NULL in this case) to mark end of a level.
Algorithm:
1. Put root in queue.
2. Put NULL in queue.
3. While Queue is not empty
4. x = fetch first element from queue
5. If x is not NULL
6. x->rpeer <= top element of queue.
7. put left and right child of x in queue
8. else
9. if queue is not empty
10. put NULL in queue
11. end if
12. end while
13. return
#include <queue>
void print(tree* root)
{
queue<tree*> que;
if (!root)
return;
tree *tmp, *l, *r;
que.push(root);
que.push(NULL);
while( !que.empty() )
{
tmp = que.front();
que.pop();
if(tmp != NULL)
{
cout << tmp=>val; //print value
l = tmp->left;
r = tmp->right;
if(l) que.push(l);
if(r) que.push(r);
}
else
{
if (!que.empty())
que.push(NULL);
}
}
return;
}