I'am using Developer Express XtraGrid Component to show some data. I have 2 XtraGrid on my Windows Application Form. Both grids have more than 200k+ lines, and 8 columns of data, and I have export to excel button. There are two ways (as I know) for exporting grid data to excel.
1- grid.ExportToXls(); or grid.ExportToXlsx();
2- Using Office Interop, and OpenXML Utilities
If I use grid.ExportToXls(); or grid.ExportToXlsx();, the process time is faster than Office Interop Codes (for arround 2k lines of data). But, this method can be used for just 1 grid. So result appears on 2 different Excel files. So, I'am using Office Interop to merge workbooks after process completed. Here is the problem occurs. With both these ways, I am always getting System.OutOfMemory Exception. (See the memory graph below)
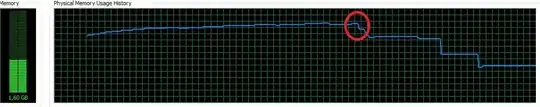
I'am stuck here, because the ways I know to export excel are throwing System.OutOfMemory Exception. Do you have any suggestion, how can I export more than 200k - 300k+ lines of data to Excel? I'am using .Net Framework 3.5 on Visual Studio 2010.
And you can find my Interop, and Document.Format OpenXML Utility codes below.
try
{
SaveFileDialog saveDialog = new SaveFileDialog();
saveDialog.Title = SaveAsTitle;
saveDialog.Filter = G.Instance.MessageManager.GetResourceMessage("EXCEL_FILES_FILTER");
saveDialog.ShowDialog();
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(saveDialog.FileName))
{
// Showing Warning
return;
}
List<GridControl> exportToExcel = new List<GridControl>();
exportToExcel.Add(dataGrid);
exportToExcel.Add(summaryGrid);
ExportXtraGridToExcel2007(saveDialog.FileName, exportToExcel);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// Showing Error
}
And this is my ExportXtraGridToExcel2007(); function codes
public void ExportXtraGridToExcel2007(string path, List<GridControl> grids)
{
try
{
DisableMdiParent();
string tmpPath = Path.GetTempPath();
List<string> exportedFiles = new List<string>();
for (int i = 0; i < grids.Count; i++)
{
string currentPath = string.Format(@"{0}\document{1}.xlsx", tmpPath, i);
GridControl grid = grids[i];
grid.MainView.ExportToXlsx(currentPath);
exportedFiles.Add(currentPath);
}
if (exportedFiles.Count > 0)
{
OpenXmlUtilities.MergeWorkbooks(path, exportedFiles.ToArray());
foreach (string excel in exportedFiles)
{
if (File.Exists(excel))
{
try
{
File.Delete(excel);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
EventLog.WriteEntry("Application", ex.Message);
}
}
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// showing error
}
finally
{
EnableMdiParent();
}
}
and this is the OpenXML Merge Work Books Codes
public static void MergeWorkbooks(string path, string[] sourceWorkbookNames)
{
WorkbookPart mergedWorkbookPart = null;
WorksheetPart mergedWorksheetPart = null;
WorksheetPart childWorksheetPart = null;
Sheets mergedWorkbookSheets = null;
Sheets childWorkbookSheets = null;
Sheet newMergedSheet = null;
SheetData mergedSheetData = null;
SharedStringTablePart mergedSharedStringTablePart = null;
SharedStringTablePart childSharedStringTablePart = null;
// Create the merged workbook package.
using (SpreadsheetDocument mergedWorkbook =
SpreadsheetDocument.Create(path,
SpreadsheetDocumentType.Workbook))
{
// Add the merged workbook part to the new package.
mergedWorkbookPart = mergedWorkbook.AddWorkbookPart();
GenerateMergedWorkbook().Save(mergedWorkbookPart);
// Get the Sheets element in the merged workbook for use later.
mergedWorkbookSheets = mergedWorkbookPart.Workbook.GetFirstChild<Sheets>();
// Create the Shared String Table part in the merged workbook.
mergedSharedStringTablePart = mergedWorkbookPart.AddNewPart<SharedStringTablePart>();
GenerateSharedStringTablePart().Save(mergedSharedStringTablePart);
// For each source workbook to merge...
foreach (string workbookName in sourceWorkbookNames)
{
// Open the source workbook. The following will throw an exception if
// the source workbook does not exist.
using (SpreadsheetDocument childWorkbook =
SpreadsheetDocument.Open(workbookName, false))
{
// Get the Sheets element in the source workbook.
childWorkbookSheets = childWorkbook.WorkbookPart.Workbook.GetFirstChild<Sheets>();
// Get the Shared String Table part of the source workbook.
childSharedStringTablePart = childWorkbook.WorkbookPart.SharedStringTablePart;
// For each worksheet in the source workbook...
foreach (Sheet childSheet in childWorkbookSheets)
{
// Get a worksheet part for the source worksheet using it's relationship Id.
childWorksheetPart = (WorksheetPart)childWorkbook.WorkbookPart.GetPartById(childSheet.Id);
// Add a worksheet part to the merged workbook based on the source worksheet.
mergedWorksheetPart = mergedWorkbookPart.AddPart<WorksheetPart>(childWorksheetPart);
// There should be only one worksheet that is set as the main view.
CleanView(mergedWorksheetPart);
// Create a Sheet element for the new sheet in the merged workbook.
newMergedSheet = new Sheet();
// Set the Name, Id, and SheetId attributes of the new Sheet element.
newMergedSheet.Name = GenerateWorksheetName(mergedWorkbookSheets, childSheet.Name.Value);
newMergedSheet.Id = mergedWorkbookPart.GetIdOfPart(mergedWorksheetPart);
newMergedSheet.SheetId = (uint)mergedWorkbookSheets.ChildElements.Count + 1;
// Add the new Sheet element to the Sheets element in the merged workbook.
mergedWorkbookSheets.Append(newMergedSheet);
// Get the SheetData element of the new worksheet part in the merged workbook.
mergedSheetData = mergedWorksheetPart.Worksheet.GetFirstChild<SheetData>();
// For each row of data...
foreach (Row row in mergedSheetData.Elements<Row>())
{
// For each cell in the row...
foreach (Cell cell in row.Elements<Cell>())
{
// If the cell is using a shared string then merge the string
// from the source workbook into the merged workbook.
if (cell.DataType != null &&
cell.DataType.Value == CellValues.SharedString)
{
ProcessCellSharedString(mergedWorksheetPart, cell,
mergedSharedStringTablePart, childSharedStringTablePart);
}
}
}
}
}
}
//Save the changes to the merged workbook.
mergedWorkbookPart.Workbook.Save();
}
}