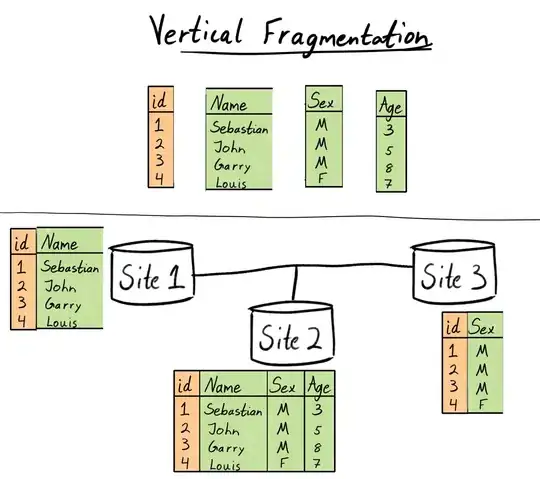
I'm new to Azure's function... I've created a new timer function (will be fired every 30 minutes) and it has to perform a query on a URL, then push data on the buffer..
I've done
public static void Run(TimerInfo myTimer, TraceWriter log)
{
var s = CloudConfigurationManager.GetSetting("url");
log.Info(s);
}
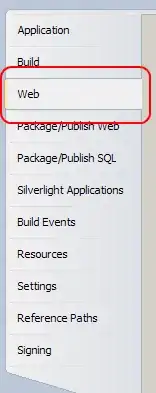
And in my function settings I've
What am I doing wrong? Thanks