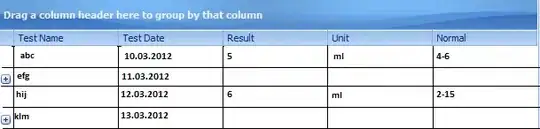
I have this kind of pandas DataFrame for each user in a large database.
each row is a period of length [start_date, end_date], but sometimes 2 consecutive rows are in fact the same period : end_date is equal to the following start_date (red underlining). Sometimes periods even overlap on more than 1 date.
I would like to get the "real periods" by combining rows which corresponds to the same periods.
What I have tried
def split_range(name):
df_user = de_201512_echant[de_201512_echant.name == name]
# -- Create a date_range with a length [min_start_date, max_start_date]
t_date = pd.DataFrame(index=pd.date_range("2005-01-01", "2015-12-12").date)
for row in range(0, df_user.shape[0]):
start_date = df_user.iloc[row].start_date
end_date = df_user.iloc[row].end_date
if ((pd.isnull(start_date) == False) and (pd.isnull(end_date) == False)):
t = pd.DataFrame(index=pd.date_range(start_date, end_date))
t["period_%s" % (row)] = 1
t_date = pd.merge(t_date, t, right_index=True, left_index=True, how="left")
else:
pass
return t_date
which yields a DataFrame where each colunms is a period (1 if in the range, NaN if not) :
t_date
Out[29]:
period_0 period_1 period_2 period_3 period_4 period_5 \
2005-01-01 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
2005-01-02 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
2005-01-03 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
2005-01-04 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
2005-01-05 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
2005-01-06 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
2005-01-07 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
2005-01-08 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
2005-01-09 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
2005-01-10 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
2005-01-11 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
Then if I sum all the columns (periods) I got almost exactly what I want :
full_spell = t_date.sum(axis=1)
full_spell.loc[full_spell == 1]
Out[31]:
2005-11-14 1.0
2005-11-15 1.0
2005-11-16 1.0
2005-11-17 1.0
2005-11-18 1.0
2005-11-19 1.0
2005-11-20 1.0
2005-11-21 1.0
2005-11-22 1.0
2005-11-23 1.0
2005-11-24 1.0
2005-11-25 1.0
2005-11-26 1.0
2005-11-27 1.0
2005-11-28 1.0
2005-11-29 1.0
2005-11-30 1.0
2006-01-16 1.0
2006-01-17 1.0
2006-01-18 1.0
2006-01-19 1.0
2006-01-20 1.0
2006-01-21 1.0
2006-01-22 1.0
2006-01-23 1.0
2006-01-24 1.0
2006-01-25 1.0
2006-01-26 1.0
2006-01-27 1.0
2006-01-28 1.0
2015-07-06 1.0
2015-07-07 1.0
2015-07-08 1.0
2015-07-09 1.0
2015-07-10 1.0
2015-07-11 1.0
2015-07-12 1.0
2015-07-13 1.0
2015-07-14 1.0
2015-07-15 1.0
2015-07-16 1.0
2015-07-17 1.0
2015-07-18 1.0
2015-07-19 1.0
2015-08-02 1.0
2015-08-03 1.0
2015-08-04 1.0
2015-08-05 1.0
2015-08-06 1.0
2015-08-07 1.0
2015-08-08 1.0
2015-08-09 1.0
2015-08-10 1.0
2015-08-11 1.0
2015-08-12 1.0
2015-08-13 1.0
2015-08-14 1.0
2015-08-15 1.0
2015-08-16 1.0
2015-08-17 1.0
dtype: float64
But I could not find a way to slice all the time range of this sparse datetime index to finally get my desired output : the original dataframe containing the "real" period of time.
It might not be the most efficient way to do this, so If you have alternatives, do not hesitate!