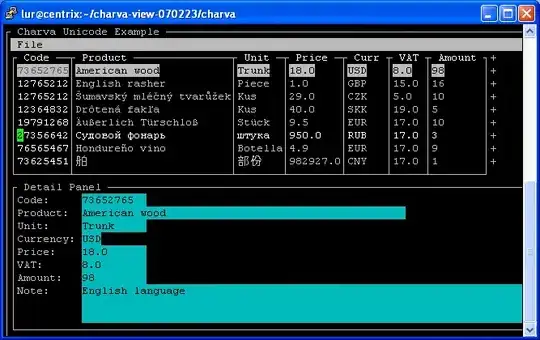
I have a numpy array that looks like this.

I want to interpolate between data points to fill some smaller holes in the data. Let's say in this example I want to interpolate over a maximum of 2 pixels. Then I would expect something similar to this.
So far I've tried several interpolation methods like:
from scipy.interpolate import LinearNDInterpolator
valid_mask = ~np.isnan(raw)
coords = np.array(np.nonzero(valid_mask)).T
values = raw[valid_mask]
it = LinearNDInterpolator(coords, values)
interpolated = it(list(np.ndindex(raw.shape))).reshape(raw.shape)
This approach doesn't preserve clusters in the data, which I could easyly overcome by clustering beforehand and then adding the results. But more importantly it interpolates over high distances in clusters that have a concave form.
Could anyone point out to me an interpolation method that used some kind of distance threshold?
For testing I included the sample data that I used to explain my problem:
raw = np.array([[ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 0., 0., 3., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 5., 4., 4., 4., 4., 4., 5.],
[ 0., 5., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]])
raw[raw==0]=np.nan