Logarithmic Least Squares
Since we can convert a logarithmic function into a line by taking the log of the x values, we can perform a linear least squares curve fitting. In fact, the work has been done for us and a solution is presented at Math World.
In brief, we're given $X and $Y values that are from a distribution like y = a + b * log(x). The least squares method will give some values aFit and bFit that minimize the distance from the parametric curve to the data points given.
Here is an example implementation in PHP:
First I'll generate some random data with known underlying distribution given by $a and $b
// True parameter valaues
$a = 10;
$b = 5;
// Range of x values to generate
$x_min = 1;
$x_max = 10;
$nPoints = 50;
// Generate some random points on y = a * log(x) + b
$X = array();
$Y = array();
for($p = 0; $p < $nPoints; $p++){
$x = $p / $nPoints * ($x_max - $x_min) + $x_min;
$y = $a + $b * log($x);
$X[] = $x + rand(0, 200) / ($nPoints * $x_max);
$Y[] = $y + rand(0, 200) / ($nPoints * $x_max);
}
Now, here's how to use the equations given to estimate $a and $b.
// Now convert to log-scale for X
$logX = array_map('log', $X);
// Now estimate $a and $b using equations from Math World
$n = count($X);
$square = create_function('$x', 'return pow($x,2);');
$x_squared = array_sum(array_map($square, $logX));
$xy = array_sum(array_map(create_function('$x,$y', 'return $x*$y;'), $logX, $Y));
$bFit = ($n * $xy - array_sum($Y) * array_sum($logX)) /
($n * $x_squared - pow(array_sum($logX), 2));
$aFit = (array_sum($Y) - $bFit * array_sum($logX)) / $n;
You may then generate points for your Javascript as densely as you like:
$Yfit = array();
foreach($X as $x) {
$Yfit[] = $aFit + $bFit * log($x);
}
In this case, the code estimates bFit = 5.17 and aFit = 9.7, which is quite close for only 50 data points.
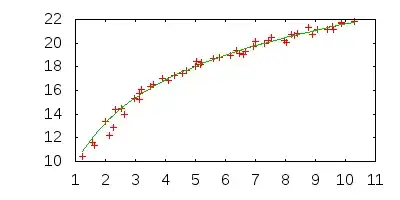
For the example data given in the comment below, a logarithmic function does not fit well.
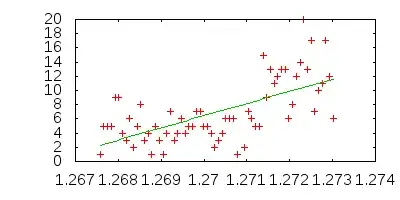
The least squares solution is y = -514.734835478 + 2180.51562281 * log(x) which is essentially a line in this domain.

