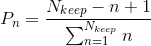It has been already recognized that your problem amounts at a cumulative summation. Following Robert Crovella's comment, I just want to provide an example of use of CUDA Thrust's thrust::inclusive_scan for the computation of a cumulative summation.
The example refers to the case when you want to apply rank weigthing to a genetic algorithm. In this case, you rank the chromosomes and set up the following probability
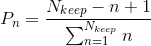
and from that probability distribution you calculate the cumulative probability. See
R.L. Haupt, S.E. Haupt, "Practical Genetic Algorithms, Second Edition", J. Wiley and Sons, pp. 39
#include <thrust/device_vector.h>
#include <thrust/transform.h>
#include <thrust/functional.h>
#include <thrust/iterator/counting_iterator.h>
#include <thrust/iterator/constant_iterator.h>
#include <cstdio>
template <class T>
struct scaling {
const T _a;
scaling(T a) : _a(a) { }
__host__ __device__ T operator()(const T &x) const { return _a * x; }
};
void main()
{
const int N = 20;
double a = -(double)N;
double b = 0.;
double Dx = -1./(0.5*N*(N+1));
thrust::device_vector<double> MatingProbability(N);
thrust::device_vector<double> CumulativeProbability(N+1, 0.);
thrust::transform(thrust::make_counting_iterator(a), thrust::make_counting_iterator(b), MatingProbability.begin(), scaling<double>(Dx));
thrust::inclusive_scan(MatingProbability.begin(), MatingProbability.end(), CumulativeProbability.begin() + 1);
for(int i=0; i<N+1; i++)
{
double val = CumulativeProbability[i];
printf("%d %3.15f\n", i, val);
}
}
Other examples of cumulative summations regard the numerical calculation of the primitive of a function.