How to find third or nth maximum salary from salary table(EmpID, EmpName, EmpSalary) in optimized way?
- 15,447
- 5
- 79
- 98
- 1,494
- 2
- 12
- 20
-
3http://stackoverflow.com/questions/3617152/t-sql-how-to-select-only-first-or-second-row-from-a-table – Apr 26 '13 at 11:13
-
2```SELECT salary FROM (SELECT salary FROM employee ORDER BY salary DESC FETCH NEXT 3 ROWS ONLY) ORDER BY salary ASC FETCH NEXT 1 ROWS ONLY;``` – Sathvik Sep 10 '20 at 17:43
56 Answers
Row Number :
SELECT Salary,EmpName
FROM
(
SELECT Salary,EmpName,ROW_NUMBER() OVER(ORDER BY Salary) As RowNum
FROM EMPLOYEE
) As A
WHERE A.RowNum IN (2,3)
Sub Query :
SELECT *
FROM Employee Emp1
WHERE (N-1) = (
SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT(Emp2.Salary))
FROM Employee Emp2
WHERE Emp2.Salary > Emp1.Salary
)
Top Keyword :
SELECT TOP 1 salary
FROM (
SELECT DISTINCT TOP n salary
FROM employee
ORDER BY salary DESC
) a
ORDER BY salary
- 16,594
- 6
- 37
- 44
- 3,746
- 3
- 37
- 42
-
how to get minimum salary record from table? select ins.KYS_ID , ins.FKYS_INS_ID from cmn_pat_x_insurance ins where ins.FKYS_PAT_ID='1253_717' and ins.FKYS_INS_TYPE in(1) and ins.BOL_TYPE in(1,3) and ins.salary in (min(ins.salary)) – saidesh kilaru Dec 11 '13 at 05:31
-
Kumar and Alexander, i want to get one more field with it, how to do that? my query is like """Select Top 1 NoteID From ( Select DateDiff(Year,SchedualDate, Current_TimeStamp) as NoteAge, Distinct Top 3 NoteID From [dbo].[DocSecheduale] Order by NoteID Desc )a Order by NoteID""" – Zaveed Abbasi Mar 25 '14 at 12:29
-
I'm finding nth highest salary but i am getting complexity to understand the sub-query, would you like to explain the sub-query ... – Deepak Gupta Mar 10 '15 at 11:51
-
@deepak_java the subquery is evaluated each and every time a row is processed by the outer query. In other words, the inner query can not be processed independently of the outer query since the inner query uses the Emp1 value as well. – Kumar Manish Mar 11 '15 at 03:30
-
Its important to understand why the `... WHERE (N-1) = (Subquery)...` works. The subquery is a correlated query since its `WHERE` clause uses `Emp1` from main query. The subquery is evaluated each time main query scans over a row. Example, if we are to find 3rd largest salary (N=3) from (800, 1000, 700, 750), the subquery for 1st row would be `SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT(Emp2.Salary)) FROM Employee Emp2 WHERE Emp2.Salary > 800` which is 0. For 4th salary value (750) `... WHERE Emp2.Salary > 750` will be 2, or N-1, hence this row will be returned. – jerrymouse Sep 04 '16 at 18:46
-
Is the ORDER BY salary still necessary? Because you are only getting 1 value because of TOP 1 – brijmcq Apr 02 '17 at 13:24
-
http://www.programmerinterview.com/index.php/database-sql/find-nth-highest-salary-sql has very good explanation on how the co-related sub query is working – Naresh Joshi Nov 22 '17 at 11:02
Use ROW_NUMBER(if you want a single) or DENSE_RANK(for all related rows):
WITH CTE AS
(
SELECT EmpID, EmpName, EmpSalary,
RN = ROW_NUMBER() OVER (ORDER BY EmpSalary DESC)
FROM dbo.Salary
)
SELECT EmpID, EmpName, EmpSalary
FROM CTE
WHERE RN = @NthRow
- 450,073
- 74
- 686
- 939
-
how to get minimum salary record from table? select ins.KYS_ID , ins.FKYS_INS_ID from cmn_pat_x_insurance ins where ins.FKYS_PAT_ID='1253_717' and ins.FKYS_INS_TYPE in(1) and ins.BOL_TYPE in(1,3) and ins.salary in (min(ins.salary)) – saidesh kilaru Dec 11 '13 at 05:32
-
Imagine , there are 10,0000 records in employee table. If I use the above query , the performance will be reduced by 6-10 times. – Bimal Das Nov 27 '17 at 06:50
-
2@BimalDas: then you don't have an index on the `EmpSalary` column. Also, reduced compared to what? The advantage of the `ROW_NUMBER` approach is that you can use `..OVER(PARTITION BY GroupColumn OrderBy OrderColumn)`. So you can use it to get groups but still access any column of it. – Tim Schmelter Nov 27 '17 at 09:14
-
@TimSchmelter WITH CTE will create a temporary table to store entire data of first SELECT statement into it , then from the result we selecting "SELECT EmpID, EmpName, EmpSalary FROM CTE WHERE RN = @NthRow" . That is why I guess it is little slow. I checked it. and I also have proper indexing. – Bimal Das Nov 27 '17 at 11:03
-
2@BimalDas: No, it's not creating a temporary table. A cte is normally not materialized anywhere. It's more like an inline view or named subquery. – Tim Schmelter Nov 27 '17 at 11:14
-
@BimalDas: ask a question on stackoverflow and provide all relevant informations (like schema and query execution plan, upload [here](https://www.brentozar.com/pastetheplan/)). – Tim Schmelter Nov 27 '17 at 11:34
-
Sorry, I am learning SQL and I am confused by why we can't for example do something simpler like: `SELECT * FROM table ORDER BY EmpSalary DESC LIMIT 2, 1`. Care to explain why the answer here is the best answer (and what if any are the flaws with my suggestion)? – Feb 08 '18 at 02:39
-
2@KennyLJ: well, this was a SQL-Server question and `LIMIT` is MySql. In MS-SQL-Server you need a sub-query or CTE because you can't use `ROW_NUMBER` in the `WHERE`. [Why you can’t use `ROW_NUMBER()` In the `WHERE` Clause](https://www.sqltheater.com/2017/09/28/cant-use-row_number-where/) – Tim Schmelter Feb 08 '18 at 08:53
Try this
SELECT TOP 1 salary FROM (
SELECT TOP 3 salary
FROM employees
ORDER BY salary DESC) AS emp
ORDER BY salary ASC
For 3 you can replace any value...
-
does this work with oracle 10g or 11g? Or is there an alternative which is pretty like this? – RBz Sep 28 '18 at 12:15
If you want optimize way means use TOP Keyword, So the nth max and min salaries query as follows but the queries look like a tricky as in reverse order by using aggregate function names:
N maximum salary:
SELECT MIN(EmpSalary)
FROM Salary
WHERE EmpSalary IN(SELECT TOP N EmpSalary FROM Salary ORDER BY EmpSalary DESC)
for Ex: 3 maximum salary:
SELECT MIN(EmpSalary)
FROM Salary
WHERE EmpSalary IN(SELECT TOP 3 EmpSalary FROM Salary ORDER BY EmpSalary DESC)
N minimum salary:
SELECT MAX(EmpSalary)
FROM Salary
WHERE EmpSalary IN(SELECT TOP N EmpSalary FROM Salary ORDER BY EmpSalary ASC)
for Ex: 3 minimum salary:
SELECT MAX(EmpSalary)
FROM Salary
WHERE EmpSalary IN(SELECT TOP 3 EmpSalary FROM Salary ORDER BY EmpSalary ASC)
- 659
- 5
- 10
-
-
4to get the max salary why we are doing in ASC order , it has to be done in DESC order , if we have salary like this 7000,10000,11000,500,800,900,12000 , then inner query of sorting will result in top3 that means 500,800,900 and max of these is 900, but 900 is not the 3 maximum , 3 maximum salary is 10000. – Narendra Jaggi Feb 28 '18 at 18:55
-
1for Ex: 3 maximum salaries: It has to be like that SELECT Min(EmpSalary) FROM Salary WHERE EmpSalary IN(SELECT TOP 3 EmpSalary FROM Salary ORDER BY EmpSalary DESC) – Jimit Rupani Aug 06 '18 at 17:57
-
Too simple if you use the sub query!
SELECT MIN(EmpSalary) from (
SELECT EmpSalary from Employee ORDER BY EmpSalary DESC LIMIT 3
);
You can here just change the nth value after the LIMIT constraint.
Here in this the Sub query Select EmpSalary from Employee Order by EmpSalary DESC Limit 3; would return the top 3 salaries of the Employees. Out of the result we will choose the Minimum salary using MIN command to get the 3rd TOP salary of the employee.
- 1,377
- 2
- 18
- 43
-
Getting this error. Error Code : 1248 Every derived table must have its own alias – Nov 03 '15 at 04:08
-
add an alias to it.. SELECT MIN(EmpSalary) from ( SELECT EmpSalary from Employee ORDER BY EmpSalary DESC LIMIT 3 ) as s; – Dev Utkarsh Nov 03 '15 at 19:19
-
Just use DISTINCT to avoid duplicates SELECT MIN(EmpSalary) from ( SELECT DISTINCT(EmpSalary) from Employee ORDER BY EmpSalary DESC LIMIT 3 ); – Kalpesh Parikh Mar 22 '18 at 06:04
Replace N with your Max Number
SELECT *
FROM Employee Emp1
WHERE (N-1) = (
SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT(Emp2.Salary))
FROM Employee Emp2
WHERE Emp2.Salary > Emp1.Salary)
Explanation
The query above can be quite confusing if you have not seen anything like it before – the inner query is what’s called a correlated sub-query because the inner query (the subquery) uses a value from the outer query (in this case the Emp1 table) in it’s WHERE clause.
And Source
- 11,389
- 16
- 53
- 71
-
2+1 Its important to understand why the `... WHERE (N-1) = (Subquery)...` works. The subquery is a correlated query since its `WHERE` clause uses `Emp1` from main query. The subquery is evaluated each time main query scans over a row. Example, if we are to find 3rd largest salary (N=3) from (800, 1000, 700, 750), the subquery for 1st row would be `SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT(Emp2.Salary)) FROM Employee Emp2 WHERE Emp2.Salary > 800` which is 0. For 4th salary value (750) `... WHERE Emp2.Salary > 750` will be 2, or N-1, hence this row will be returned. – jerrymouse Sep 04 '16 at 18:49
-
`SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT(Emp2.Salary)) FROM Employee Emp2 WHERE Emp2.Salary > 800 which is 0.` It will be 1. – Shad Dec 20 '20 at 09:16
Third or nth maximum salary from salary table without using subquery
select salary from salary
ORDER BY salary DESC
OFFSET N-1 ROWS
FETCH NEXT 1 ROWS ONLY
For 3rd highest salary put 2 in place of N-1
- 16,753
- 12
- 73
- 90
- 137
- 1
- 3
-
3Important to mention that OFFSET FETCH is available from SQL Server 2012 + version. – Zerotoinfinity Aug 31 '15 at 12:57
SELECT Salary,EmpName
FROM
(
SELECT Salary,EmpName,DENSE_RANK() OVER(ORDER BY Salary DESC) Rno from EMPLOYEE
) tbl
WHERE Rno=3
- 5,698
- 8
- 32
- 54
- 119
- 1
- 2
SELECT EmpSalary
FROM salary_table
GROUP BY EmpSalary
ORDER BY EmpSalary DESC LIMIT n-1, 1;
- 5,280
- 2
- 25
- 34
- 12,712
- 6
- 88
- 78
Refer following query for getting nth highest salary. By this way you get nth highest salary in MYSQL. If you want get nth lowest salary only you need to replace DESC by ASC in the query.
- 1,351
- 13
- 13
Method 1:
SELECT TOP 1 salary FROM (
SELECT TOP 3 salary
FROM employees
ORDER BY salary DESC) AS emp
ORDER BY salary ASC
Method 2:
Select EmpName,salary from
(
select EmpName,salary ,Row_Number() over(order by salary desc) as rowid
from EmpTbl)
as a where rowid=3
-
Method 1 can be sort: SELECT TOP 1 SALARY FROM (SELECT TOP 3 SALARY FROM EMPLOYEES) *reason- because by default its ascending order – Ashish Agrawal Yodlee Mar 15 '19 at 16:25
In 2008 we can use ROW_NUMBER() OVER (ORDER BY EmpSalary DESC) to get a rank without ties that we can use.
For example we can get the 8th highest this way, or change @N to something else or use it as a parameter in a function if you like.
DECLARE @N INT = 8;
WITH rankedSalaries AS
(
SELECT
EmpID
,EmpName
,EmpSalary,
,RN = ROW_NUMBER() OVER (ORDER BY EmpSalary DESC)
FROM salary
)
SELECT
EmpID
,EmpName
,EmpSalary
FROM rankedSalaries
WHERE RN = @N;
In SQL Server 2012 as you might know this is performed more intuitively using LAG().
- 978
- 8
- 14
Answering this question from the point of view of SQL Server as this is posted in the SQL Server section.
There many approaches of getting Nth salary and we can classify these approaches in two sections one using ANSI SQL approach and other using TSQL approach. You can also check out this find nth highest salary youtube video which shows things practically. Let’s try to cover three ways of writing this SQL.
- Approach number 1: - ANSI SQL: - Using Simple order by and top keyword.
- Approach number 2: - ANSI SQL: - Using Co-related subqueries.
- Approach number 3: - TSQL: - using Fetch Next
Approach number 1: - Using simple order by and top.
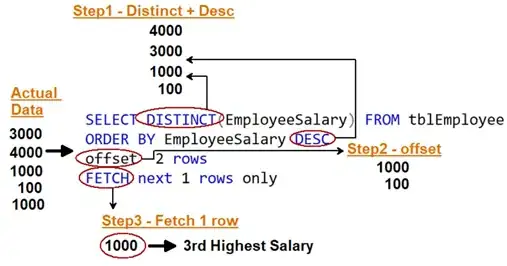
In this approach we will using combination of order by and top keyword. We can divide our thinking process in to 4 steps: -
Step 1: - Descending :- Whatever data we have first make it descending by using order by clause.
Step 2:- Then use TOP keyword and select TOP N. Where N stands for which highest salary rank you want.
Step 3: - Ascending: - Make the data ascending.
Step 4:- Select top 1 .There you are done.
So, if you put down the above 4 logical steps in SQL it comes up something as shown below.
Below is the text of SQL in case you want to execute and test the same.
select top 1 * from (select top 2 EmployeeSalary from tblEmployee order by EmployeeSalary desc) as innerquery order by EmployeeSalary asc
Parameterization issue of Approach number 1
One of the biggest issues of Approach number 1 is “PARAMETERIZATION”.
If you want to wrap up the above SQL in to a stored procedure and give input which top salary you want as a parameter, it would be difficult by Approach number 1.
One of the things you can do with Approach number 1 is make it a dynamic SQL but that would not be an elegant solution. Let’s check out Approach number 2 which is an ANSI SQL approach.
Approach number 2: - Using Co-related subqueries.
Below is how co-related subquery solution will look like. In case you are new to Co-related subquery. Co-related subquery is a query which a query inside query. The outer query first evaluates, sends the record to the inner query, inner query then evaluates and sends it to the outer query.
“3” in the query is the top salary we want to find out.
Select E1.EmployeeSalary from tblEmployee as E1 where 3=(Select count(*) from tblEmployee as E2 Where E2.EmployeeSalary>=E1.EmployeeSalary)
So in the above query we have an outer query:-
Select E1.EmployeeSalary from tblEmployee as E1
and inner query is in the where clause. Watch those BOLD’s which indicate how the outer table alias is referred in the where clause which makes co-related evaluate inner and outer query to and fro: -
where 3=(Select count(*) from tblEmployee as E2 Where E2.EmployeeSalary>=E1.EmployeeSalary)
So now let’s say you have records like 3000, 4000 ,1000 and 100 so below will be the steps: -
- First 3000 will be send to the inner query.
- Inner query will now check how many record values are greater than or equal to 3000. If the number of record counts is not equal, it will take next value which is 4000. Now for 3000 there are only 2 values which is greater than or equal, 3000 and 4000. So, Is number record count 2>-=3? .NO, so it takes second value which is 4000.
- Again for 4000 how many record values are greater than or equal. If the number of record count is not equal, it will take next value which is 1000.
- Now 1000 has 3 records more or equal than 1000, (3000,4000 and 1000 himself). This is where co-related stops and exits and gives the final output.
Approach number 3: - TSQL fetch and Next.
Third approach is by using TSQL. By using Fetch and Next, we can get the Nth highest easily.
But please do note, TSQL code will not work for other databases we will need to rewrite the whole code again.
It would be a three-step process:-
Step 1 Distinct and Order by descending: - First apply distinct and order by which made the salaries descending as well as weed off the duplicates.
Step 2 Use Offset: - Use TSQL Offset and get the top N-1 rows. Where N is the highest salary we want to get. Offset takes the number of rows specified, leaving the other rows. Why (N-1) because it starts from zero.
Step 3 Use Fetch: - Use fetch and get the first row. That row has the highest salary.
The SQL looks something as shown below.
Performance comparison
Below is the SQL plan for performance comparison. Below is the plan for top and order by.
Below is the plan for co-related queries. You can see the number of operators are quiet high in numbers. So surely co-related would perform bad for huge data.
Below is TSQL query plan which is better than cor-related.
So, summing up we can compare more holistically as given in the below table.
- 27,644
- 7
- 84
- 73
declare @maxNthSal as nvarchar(20)
SELECT TOP 3 @maxNthSal=GRN_NAME FROM GRN_HDR ORDER BY GRN_NAME DESC
print @maxNthSal
- 297,002
- 52
- 306
- 350
- 65
- 1
To get third highest value from table
SELECT * FROM tableName ORDER BY columnName DESC LIMIT 2, 1
- 612
- 10
- 15
-
SELECT Distinct columnName FROM tableName ORDER BY columnName DESC LIMIT 2, 1 – Devendra Singraul Nov 08 '19 at 17:17
This is one of the popular question in any SQL interview. I am going to write down different queries to find out the nth highest value of a column.
I have created a table named “Emloyee” by running the below script.
CREATE TABLE Employee([Eid] [float] NULL,[Ename] [nvarchar](255) NULL,[Basic_Sal] [float] NULL)
Now I am going to insert 8 rows into this table by running below insert statement.
insert into Employee values(1,'Neeraj',45000)
insert into Employee values(2,'Ankit',5000)
insert into Employee values(3,'Akshay',6000)
insert into Employee values(4,'Ramesh',7600)
insert into Employee values(5,'Vikas',4000)
insert into Employee values(7,'Neha',8500)
insert into Employee values(8,'Shivika',4500)
insert into Employee values(9,'Tarun',9500)
Now we will find out 3rd highest Basic_sal from the above table using different queries. I have run the below query in management studio and below is the result.
select * from Employee order by Basic_Sal desc
We can see in the above image that 3rd highest Basic Salary would be 8500. I am writing 3 different ways of doing the same. By running all three mentioned below queries we will get same result i.e. 8500.
First Way: - Using row number function
select Ename,Basic_sal
from(
select Ename,Basic_Sal,ROW_NUMBER() over (order by Basic_Sal desc) as rowid from Employee
)A
where rowid=2
- 170,088
- 45
- 397
- 571
- 391
- 4
- 14
Select TOP 1 Salary as '3rd Highest Salary' from (SELECT DISTINCT TOP 3 Salary from Employee ORDER BY Salary DESC) a ORDER BY Salary ASC;
I am showing 3rd highest salary
- 92
- 1
- 3
- 12
SELECT MIN(COLUMN_NAME)
FROM (
SELECT DISTINCT TOP 3 COLUMN_NAME
FROM TABLE_NAME
ORDER BY
COLUMN_NAME DESC
) AS 'COLUMN_NAME'
- 6,256
- 10
- 65
- 87
- 61
- 3
--nth highest salary
select *
from (select lstName, salary, row_number() over( order by salary desc) as rn
from employee) tmp
where rn = 2
--(nth -1) highest salary
select *
from employee e1
where 1 = (select count(distinct salary)
from employee e2
where e2.Salary > e1.Salary )
Optimized way: Instead of subquery just use limit.
select distinct salary from employee order by salary desc limit nth, 1;
See limit syntax here http://www.mysqltutorial.org/mysql-limit.aspx
- 537
- 5
- 12
By subquery:
SELECT salary from
(SELECT rownum ID, EmpSalary salary from
(SELECT DISTINCT EmpSalary from salary_table order by EmpSalary DESC)
where ID = nth)
- 2,452
- 2
- 25
- 29
Try this Query
SELECT DISTINCT salary
FROM emp E WHERE
&no =(SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT salary)
FROM emp WHERE E.salary <= salary)
Put n= which value you want
- 2,536
- 3
- 22
- 36
- 51
- 1
- 7
set @n = $n
SELECT a.* FROM ( select a.* , @rn = @rn+1 from EMPLOYEE order by a.EmpSalary desc ) As a where rn = @n
- 12,712
- 6
- 88
- 78
MySQL tested solution, assume N = 4:
select min(CustomerID) from (SELECT distinct CustomerID FROM Customers order by CustomerID desc LIMIT 4) as A;
Another example:
select min(country) from (SELECT distinct country FROM Customers order by country desc limit 3);
- 639
- 9
- 19
Try this code :-
SELECT *
FROM one one1
WHERE ( n ) = ( SELECT COUNT( one2.salary )
FROM one one2
WHERE one2.salary >= one1.salary
)
- 221
- 3
- 17
Find Nth highest salary from a table. Here is a way to do this task using dense_rank() function.
select linkorder from u_links
select max(linkorder) from u_links
select max(linkorder) from u_links where linkorder < (select max(linkorder) from u_links)
select top 1 linkorder
from ( select distinct top 2 linkorder from u_links order by linkorder desc) tmp
order by linkorder asc
DENSE_RANK : 1. DENSE_RANK computes the rank of a row in an ordered group of rows and returns the rank as a NUMBER. The ranks are consecutive integers beginning with 1. 2. This function accepts arguments as any numeric data type and returns NUMBER. 3. As an analytic function, DENSE_RANK computes the rank of each row returned from a query with respect to the other rows, based on the values of the value_exprs in the order_by_clause. 4. In the above query the rank is returned based on sal of the employee table. In case of tie, it assigns equal rank to all the rows.
WITH result AS (
SELECT linkorder ,DENSE_RANK() OVER ( ORDER BY linkorder DESC ) AS DanseRank
FROM u_links )
SELECT TOP 1 linkorder FROM result WHERE DanseRank = 5
- 756
- 7
- 14
In SQL Server 2012+, OFFSET...FETCH would be an efficient way to achieve this:
DECLARE @N AS INT;
SET @N = 3;
SELECT
EmpSalary
FROM
dbo.Salary
ORDER BY
EmpSalary DESC
OFFSET (@N-1) ROWS
FETCH NEXT 1 ROWS ONLY
- 1,948
- 2
- 11
- 14
select * from employee order by salary desc;
+------+------+------+-----------+
| id | name | age | salary |
+------+------+------+-----------+
| 5 | AJ | 20 | 100000.00 |
| 4 | Ajay | 25 | 80000.00 |
| 2 | ASM | 28 | 50000.00 |
| 3 | AM | 22 | 50000.00 |
| 1 | AJ | 24 | 30000.00 |
| 6 | Riu | 20 | 20000.00 |
+------+------+------+-----------+
select distinct salary from employee e1 where (n) = (select count( distinct(salary) ) from employee e2 where e1.salary<=e2.salary);
Replace n with the nth highest salary as number.
- 1,416
- 6
- 21
- 38
- 55
- 9
SELECT TOP 1 salary FROM ( SELECT TOP n salary FROM employees ORDER BY salary DESC Group By salary ) AS emp ORDER BY salary ASC
(where n for nth maximum salary)
- 11,389
- 16
- 53
- 71
- 57
- 7
Just change the inner query value: E.g Select Top (2)* from Student_Info order by ClassID desc
Use for both problem:
Select Top (1)* from
(
Select Top (1)* from Student_Info order by ClassID desc
) as wsdwe
order by ClassID
- 58,085
- 24
- 103
- 107
- 1,345
- 7
- 26
- 46
To query the nth highest bonus, say n=10, using AdventureWorks2012, Try Following code
USE AdventureWorks2012;
GO
SELECT * FROM Sales.SalesPerson;
GO
DECLARE @grade INT;
SET @grade = 10;
SELECT MIN(Bonus)
FROM (SELECT TOP (@grade) Bonus FROM (SELECT DISTINCT(Bonus) FROM Sales.SalesPerson) AS a ORDER BY Bonus DESC) AS g
- 4,488
- 6
- 27
- 46
- 25
- 1
select max(sal)
from emp
where sal > (
select max(sal)
from emp
where sal > (select max(sal) from emp)
);
- 11,801
- 17
- 65
- 72
- 21
another way to find last highest data based on date
SELECT A.JID,A.EntryDate,RefundDate,Comments,Refund, ActionBy FROM (
(select JID, Max(EntryDate) AS EntryDate from refundrequested GROUP BY JID) A
Inner JOIN (SELECT JID,ENTRYDATE,refundDate,Comments,refund,ActionBy from refundrequested) B
ON A.JID=B.JID AND A.EntryDate = B.EntryDate)
- 33,544
- 126
- 357
- 626
-
i know my sql was not related to fetch nth highest salary but it show a technique to get any thing max data joining two table – Thomas Apr 02 '14 at 06:53
To find the 5th highest Salary:
Declare @N INT = 5
SELECT Salary FROM Employee
ORDER BY Salary DESC OFFSET @N - 1 ROW
- 5,952
- 3
- 43
- 62
- 21
Hi One more example to write this using common table expression:
with cte as
(SELECT TOP 3 salary
FROM salary
ORDER BY salary DESC)
select top 1 salary from cte
with cte as
(select e.Name,s.salary ,DENSE_RANK ()over ( order by salary desc) sal_rank
from salary s left join employee e
on s.EmpID=e.EmpID)
select Name,salary from cte where sal_rank=3
- 122,561
- 47
- 239
- 335
- 21
Optimized way,
;With CTE as
(
select salary
,RANK(order by salary desc) as Rnk
from table
)
select * from CTE where Rnk = @yourVariable
Second Opinion,
Declare @yourVariable int = 2
Select top 1 * from
(
select distinct top(@yourVariable) salary
from Employees
order by salary desc
)as a
order by a.salary asc
select * from Employees
order by salary desc
- 3,707
- 3
- 17
- 36
You can try this:
select top(1) EXPORT_NO
from DC_HDR
order by CASE when (ROW_NUMBER() over(order by EXPORT_NO desc))=3 then EXPORT_NO else 0 end desc
- 30,799
- 15
- 56
- 79
- 65
- 1
select min(salary)
from (select salary
from employee
where rownum < n+1
order by salary desc);
- 5,280
- 2
- 25
- 34
- 121
- 2
- 15
Showing all 3rd highest salary:
select * from emp where sal=
(SELECT DISTINCT sal FROM emp ORDER BY sal DESC LIMIT 3,1) ;
Showing only 3rd highest salary:
SELECT DISTINCT sal FROM emp ORDER BY sal DESC LIMIT 3,1
- 16,610
- 15
- 78
- 125
- 283
- 1
- 5
- 15
Try this one...
SELECT MAX(salary) FROM employee WHERE salary NOT IN (SELECT * FROM employee ORDERBY salary DESC LIMIT n-1)
- 221
- 3
- 17
SELECT * FROM (select distinct Salary from Customers order by salary DESC) limit 4,1;
Limit 4,1 means leave first 4 rows and then select the next one.
Limit and rownumber depends on the platform you are using.
Try this,it will work.
- 51
- 2
NOTE: Please replace OFFSET 3 in Query with ANY Nth integer number
SELECT EmpName,EmpSalary
FROM SALARY
ORDER BY EmpSalary DESC
OFFSET 3 ROWS
FETCH NEXT 1 ROWS ONLY
Description
FETCH NEXT 1 ROWS ONLY
return only 1 row
OFFSET 3 ROWS
exclude first 3 records Here you can you any integer number
- 991
- 7
- 20
Subqueries always take more time:
use below query to get the any highest and lowest data:
Highest Data: select *from business order by id desc limit 3,1;
Lowest data: select *from business order by id asc limit 3,1;
Can use N in the place of 3 to get nth data.
- 776
- 5
- 12
Row(s) with the nth highest salary
(assuming that multiple employees can have same salary; i.e. ties can exist)
If you want ALL the rows with the nth highest salary
select * from table_name
where salary = (
select distinct(salary) as sal from
table_name order by sal desc
limit n-1, 1
);
If you want only FIRST k rows with the nth highest salary
select * from table_name
where salary = (
select distinct(salary) as sal from
table_name order by sal desc
limit n-1, 1
) limit k; -- you can also apply `order by` in this line
Reference
- 2,374
- 1
- 30
- 33
//you can find n' th salary from table.if you want to retrive 2nd highest salary then put n=2,if 3rd hs then out n=3 as so on..
SELECT * FROM tablename t1
WHERE (N-1) = (SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT(t2.Salary))
FROM tablename t2
WHERE t2.Salary > t1.Salary)
- 33,575
- 33
- 102
- 171
- 19
finding Nth max value using CTE and FIRST_VALUE function. -- 5th max salary
;WITH CTE_NTH_SAL AS
(SELECT FIRST_VALUE(ESAL) OVER(ORDER BY ESAL DESC) AS ESAL,
1 AS ID
FROM EMPLOYEE
UNION ALL
SELECT FIRST_VALUE(EMP.ESAL) OVER(ORDER BY EMP.ESAL DESC) AS ESAL,
ID
FROM EMPLOYEE EMP,
(SELECT ESAL,
ID+1 AS ID
FROM CTE_NTH_SAL) CTE_NTH_SAL
WHERE EMP.ESAL<CTE_NTH_SAL.ESAL
AND CTE_NTH_SAL.ID<=5 )
SELECT DISTINCT ESAL
FROM CTE_NTH_SAL
WHERE ID=5
for sample result set and more ways clickhere
- 61
- 1
- 8
SELECT TOP 1 salary
FROM employee
WHERE salary IN (SELECT DISTINCT TOP 3 salary
FROM employee
ORDER BY salary DESC)
ORDER BY salary ASC
- 9,678
- 13
- 71
- 102
- 61
- 1
- 7
This is mysql query for fetching the nth highest salary from the table emp. We use "LIMIT" here as an alternative to "TOP" and the parameter (n-1) shows after which row to start from and the second parameter shows how many rows to show starting from the (n-1)th row. "LIMIT" accepts single parameter also which represents the number of rows to show starting from 0th(or 1st).
select distinct * from emp order by sal desc limit (n-1),1;
- 2,453
- 3
- 19
- 18
declare @nHighestSalary as int
set @nHighestSalary = 3
SELECT TOP 1 salary FROM (
SELECT TOP @nHighestSalary salary
FROM employees
ORDER BY salary DESC) AS emp
ORDER BY salary ASC
- 16,182
- 20
- 80
- 112
- 5
- 1
For nth highest salary..
SELECT DISTINCT Salary
FROM EMP E WHERE
n =(SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT SALARY)
FROM EMP WHERE E.SALARY <= SALARY)
n being the highest value you want, i.e 2,3 etc
- 10,152
- 30
- 45
- 67
- 35
- 1
- 2
SELECT * /*This is the outer query part */
FROM Employee Emp1
WHERE (N-1) = ( /* Subquery starts here */
SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT(Emp2.Salary))
FROM Employee Emp2
WHERE Emp2.Salary > Emp1.Salary)
- 7,479
- 3
- 37
- 69
For n-th highest value
select min(salary)
from (select salary from(select salary from employee order by salary desc)where rownum<=n);
- 122,561
- 47
- 239
- 335
- 5
- 1
select * from emp x where &no=(select count(*) from emp y where y.sal>=x.sal);
this will give take input from user and then will tell the nth maximum number.I have taken example of emp table in oracle and to display nth maximum salaried employee info
Output Enter value for no: 5
EMPNO ENAME JOB MGR HIREDATE SAL COMM DEPTNO
----- ---------- --------- ---------- --------- ---------- ---------- ----------
7698 BLAKE MANAGER 7839 01-MAY-81 3000 30
7788 SCOTT ANALYST 7566 19-APR-87 3000 20
7902 FORD ANALYST 7566 03-DEC-81 3000 20
Enter value for no: 14
EMPNO ENAME JOB MGR HIREDATE SAL COMM DEPTNO
----- ---------- --------- ---------- --------- ---------- ---------- ----------
7369 SMITH CLERK 7902 17-DEC-80 800 20
select a.GRN_NAME
from GRN_HDR a,GRN_HDR b
where a.GRN_NAME<=b.GRN_NAME
group by a.GRN_NAME
having count(a.GRN_NAME)=3
- 60,696
- 40
- 206
- 339
- 65
- 1