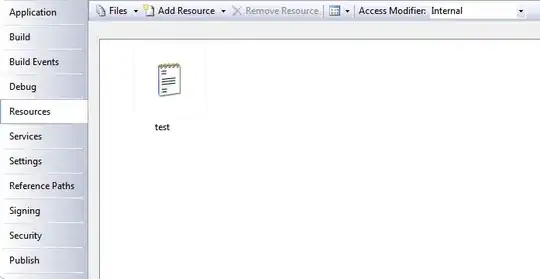
I need to read a file from my resources and add it to a list. my code:
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
using (StreamReader r = new StreamReader(Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().GetManifestResourceStream("myProg.myText.txt")))
{
//The Only Options Here Are BaseStream & CurrentEncoding
}
}
Ive searched for this and only have gotten answers like "Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly...." but my program doesnt have the option of Assembly.?