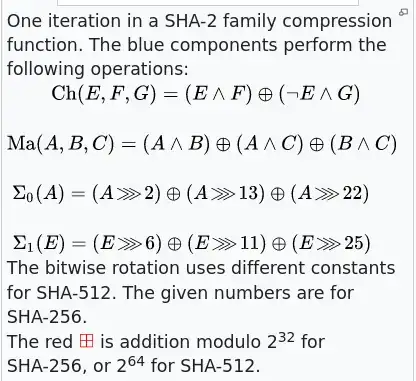
initial_hash_values=[
'6a09e667','bb67ae85','3c6ef372','a54ff53a',
'510e527f','9b05688c','1f83d9ab','5be0cd19'
]
sha_256_constants=[
'428a2f98','71374491','b5c0fbcf','e9b5dba5',
'3956c25b','59f111f1','923f82a4','ab1c5ed5',
'd807aa98','12835b01','243185be','550c7dc3',
'72be5d74','80deb1fe','9bdc06a7','c19bf174',
'e49b69c1','efbe4786','0fc19dc6','240ca1cc',
'2de92c6f','4a7484aa','5cb0a9dc','76f988da',
'983e5152','a831c66d','b00327c8','bf597fc7',
'c6e00bf3','d5a79147','06ca6351','14292967',
'27b70a85','2e1b2138','4d2c6dfc','53380d13',
'650a7354','766a0abb','81c2c92e','92722c85',
'a2bfe8a1','a81a664b','c24b8b70','c76c51a3',
'd192e819','d6990624','f40e3585','106aa070',
'19a4c116','1e376c08','2748774c','34b0bcb5',
'391c0cb3','4ed8aa4a','5b9cca4f','682e6ff3',
'748f82ee','78a5636f','84c87814','8cc70208',
'90befffa','a4506ceb','bef9a3f7','c67178f2'
]
def bin_return(dec):
return(str(format(dec,'b')))
def bin_8bit(dec):
return(str(format(dec,'08b')))
def bin_32bit(dec):
return(str(format(dec,'032b')))
def bin_64bit(dec):
return(str(format(dec,'064b')))
def hex_return(dec):
return(str(format(dec,'x')))
def dec_return_bin(bin_string):
return(int(bin_string,2))
def dec_return_hex(hex_string):
return(int(hex_string,16))
def L_P(SET,n):
to_return=[]
j=0
k=n
while k<len(SET)+1:
to_return.append(SET[j:k])
j=k
k+=n
return(to_return)
def s_l(bit_string):
bit_list=[]
for i in range(len(bit_string)):
bit_list.append(bit_string[i])
return(bit_list)
def l_s(bit_list):
bit_string=''
for i in range(len(bit_list)):
bit_string+=bit_list[i]
return(bit_string)
def rotate_right(bit_string,n):
bit_list = s_l(bit_string)
count=0
while count <= n-1:
list_main=list(bit_list)
var_0=list_main.pop(-1)
list_main=list([var_0]+list_main)
bit_list=list(list_main)
count+=1
return(l_s(list_main))
def shift_right(bit_string,n):
bit_list=s_l(bit_string)
count=0
while count <= n-1:
bit_list.pop(-1)
count+=1
front_append=['0']*n
return(l_s(front_append+bit_list))
def mod_32_addition(input_set):
value=0
for i in range(len(input_set)):
value+=input_set[i]
mod_32 = 4294967296
return(value%mod_32)
def xor_2str(bit_string_1,bit_string_2):
xor_list=[]
for i in range(len(bit_string_1)):
if bit_string_1[i]=='0' and bit_string_2[i]=='0':
xor_list.append('0')
if bit_string_1[i]=='1' and bit_string_2[i]=='1':
xor_list.append('0')
if bit_string_1[i]=='0' and bit_string_2[i]=='1':
xor_list.append('1')
if bit_string_1[i]=='1' and bit_string_2[i]=='0':
xor_list.append('1')
return(l_s(xor_list))
def and_2str(bit_string_1,bit_string_2):
and_list=[]
for i in range(len(bit_string_1)):
if bit_string_1[i]=='1' and bit_string_2[i]=='1':
and_list.append('1')
else:
and_list.append('0')
return(l_s(and_list))
def or_2str(bit_string_1,bit_string_2):
or_list=[]
for i in range(len(bit_string_1)):
if bit_string_1[i]=='0' and bit_string_2[i]=='0':
or_list.append('0')
else:
or_list.append('1')
return(l_s(or_list))
def not_str(bit_string):
not_list=[]
for i in range(len(bit_string)):
if bit_string[i]=='0':
not_list.append('1')
else:
not_list.append('0')
return(l_s(not_list))
'''
SHA-256 Specific Functions:
'''
def Ch(x,y,z):
return(xor_2str(and_2str(x,y),and_2str(not_str(x),z)))
def Maj(x,y,z):
return(xor_2str(xor_2str(and_2str(x,y),and_2str(x,z)),and_2str(y,z)))
def e_0(x):
return(xor_2str(xor_2str(rotate_right(x,2),rotate_right(x,13)),rotate_right(x,22)))
def e_1(x):
return(xor_2str(xor_2str(rotate_right(x,6),rotate_right(x,11)),rotate_right(x,25)))
def s_0(x):
return(xor_2str(xor_2str(rotate_right(x,7),rotate_right(x,18)),shift_right(x,3)))
def s_1(x):
return(xor_2str(xor_2str(rotate_right(x,17),rotate_right(x,19)),shift_right(x,10)))
def message_pad(bit_list):
pad_one = bit_list + '1'
pad_len = len(pad_one)
k=0
while ((pad_len+k)-448)%512 != 0:
k+=1
back_append_0 = '0'*k
back_append_1 = bin_64bit(len(bit_list))
return(pad_one+back_append_0+back_append_1)
def message_bit_return(string_input):
bit_list=[]
for i in range(len(string_input)):
bit_list.append(bin_8bit(ord(string_input[i])))
return(l_s(bit_list))
def message_pre_pro(input_string):
bit_main = message_bit_return(input_string)
return(message_pad(bit_main))
def message_parsing(input_string):
return(L_P(message_pre_pro(input_string),32))
def message_schedule(index,w_t):
new_word = bin_32bit(mod_32_addition([int(s_1(w_t[index-2]),2),int(w_t[index-7],2),int(s_0(w_t[index-15]),2),int(w_t[index-16],2)]))
return(new_word)
'''
This example of SHA_256 works for an input string >56 characters.
'''
def sha_256(input_string):
w_t=message_parsing(input_string)
a=bin_32bit(dec_return_hex(initial_hash_values[0]))
b=bin_32bit(dec_return_hex(initial_hash_values[1]))
c=bin_32bit(dec_return_hex(initial_hash_values[2]))
d=bin_32bit(dec_return_hex(initial_hash_values[3]))
e=bin_32bit(dec_return_hex(initial_hash_values[4]))
f=bin_32bit(dec_return_hex(initial_hash_values[5]))
g=bin_32bit(dec_return_hex(initial_hash_values[6]))
h=bin_32bit(dec_return_hex(initial_hash_values[7]))
for i in range(0,64):
if i <= 15:
t_1=mod_32_addition([int(h,2),int(e_1(e),2),int(Ch(e,f,g),2),int(sha_256_constants[i],16),int(w_t[i],2)])
t_2=mod_32_addition([int(e_0(a),2),int(Maj(a,b,c),2)])
h=g
g=f
f=e
e=mod_32_addition([int(d,2),t_1])
d=c
c=b
b=a
a=mod_32_addition([t_1,t_2])
a=bin_32bit(a)
e=bin_32bit(e)
if i > 15:
w_t.append(message_schedule(i,w_t))
t_1=mod_32_addition([int(h,2),int(e_1(e),2),int(Ch(e,f,g),2),int(sha_256_constants[i],16),int(w_t[i],2)])
t_2=mod_32_addition([int(e_0(a),2),int(Maj(a,b,c),2)])
h=g
g=f
f=e
e=mod_32_addition([int(d,2),t_1])
d=c
c=b
b=a
a=mod_32_addition([t_1,t_2])
a=bin_32bit(a)
e=bin_32bit(e)
hash_0 = mod_32_addition([dec_return_hex(initial_hash_values[0]),int(a,2)])
hash_1 = mod_32_addition([dec_return_hex(initial_hash_values[1]),int(b,2)])
hash_2 = mod_32_addition([dec_return_hex(initial_hash_values[2]),int(c,2)])
hash_3 = mod_32_addition([dec_return_hex(initial_hash_values[3]),int(d,2)])
hash_4 = mod_32_addition([dec_return_hex(initial_hash_values[4]),int(e,2)])
hash_5 = mod_32_addition([dec_return_hex(initial_hash_values[5]),int(f,2)])
hash_6 = mod_32_addition([dec_return_hex(initial_hash_values[6]),int(g,2)])
hash_7 = mod_32_addition([dec_return_hex(initial_hash_values[7]),int(h,2)])
final_hash = (hex_return(hash_0),
hex_return(hash_1),
hex_return(hash_2),
hex_return(hash_3),
hex_return(hash_4),
hex_return(hash_5),
hex_return(hash_6),
hex_return(hash_7))
return(final_hash)