Yes it does, and there is plenty of evidence to support this fact.
A ~240mL (8 oz) cup of coffee has ~150 mg caffeine (from WolframAlpha)
In a recent review of 41 studies, Ruxton (2008) finds consistent evidence that doses of coffee less than and equal to what might be found in a cup of coffee provide "improvements in physical endurance, cognitive function, particularly alertness and vigilance, mood and perception of fatigue." Here is the abstract (with bits about a secondary hypothesis related to hydration replaced by '...':
The reputed benefits of moderate caffeine consumption include
improvements in physical endurance, cognitive function, particularly
alertness and vigilance, mood and perception of fatigue... This paper is a
review of double-blind, placebo-controlled trials published over the
past 15 years to establish what range of caffeine consumption would
maximise benefits and minimise risks for cognitive function, mood,
physical performance and hydration. Of the 41 human studies meeting
the inclusion criteria, the majority reported benefits associated with
low to moderate caffeine intakes (37.5 to 450 mg per day)...
It was concluded that the range of caffeine intake
that appeared to maximise benefit and minimise risk is 38 to 400 mg
per day, equating to 1 to 8 cups of tea per day, or 0.3 to 4 cups of
brewed coffee per day. The limitations of the current evidence base
are discussed.
Another systematic literature review by Glade (2010), in which most effects were observed at doses were in the 50-200mg range (referred to as moderate), concludes:
The consumption of moderate amounts of caffeine 1) increases energy
availability, 2) increases daily energy expenditure, 3) decreases
fatigue, 4) decreases the sense of effort associated with physical
activity, 5) enhances physical performance, 6) enhances motor
performance, 7) enhances cognitive performance, 8) increases
alertness, wakefulness, and feelings of “energy,” 9) decreases mental
fatigue, 10) quickens reactions, 11) increases the accuracy of
reactions, 12) increases the ability to concentrate and focus
attention, 13) enhances short-term memory, 14) increases the ability
to solve problems requiring reasoning, 15) increases the ability to
make correct decisions, 16) enhances cognitive functioning
capabilities and neuromuscular coordination, and 17) in otherwise
healthy non-pregnant adults is safe.
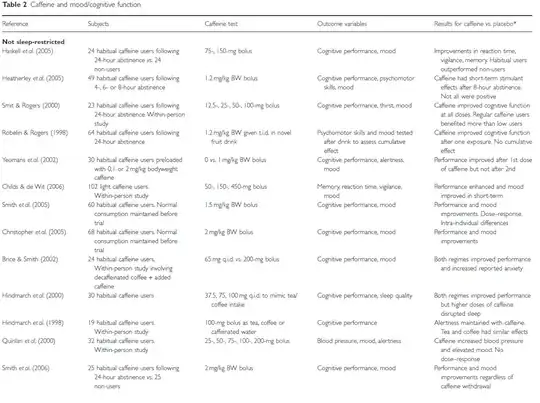
A summary of the studies on which the above conclusions are based can be found in table 2 of the Ruxton reference, the first page of this table is shown below: