From Vanderbilt University:
There is no doubt in the medical
community that it is possible to
transcutaneously, that is, through the
skin, stimulate nerves.
A variation
of EMS (electrical muscle stimulation) is transcutaneous electrical
nerve stimulation (TENS). TENS is a
pain management system that uses less
intense shocks to block pain signals.
The question about EMS is can
it really burn enough calories to
reduce a waistline, decrease body fat,
and strengthen muscles?
...
A full research study was conducted at
the University of Wisconsin and
published in 2002 by "Porcari et al".
The study was to test the claims of
EMS manufactures on there marketing of
"rock-hard abs" and other weight loss
claims.
They took 29 college aged students
that had not been in a formal exercise
program within the past 6 months and
assigned them to either a treatment
EMS group or a control group that was
given faulty EMS equipment.
The groups came in to use it 3 times
per week for 8 weeks.
The subjects used the device on five muscle groups:
- bilateral biceps
- triceps
- quadriceps
- hamstrings
- abdominal muscles
Results:
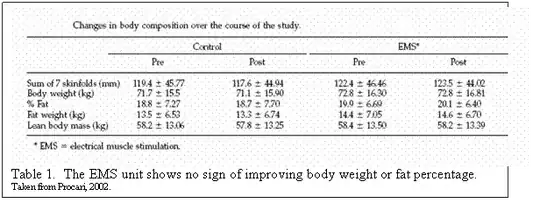
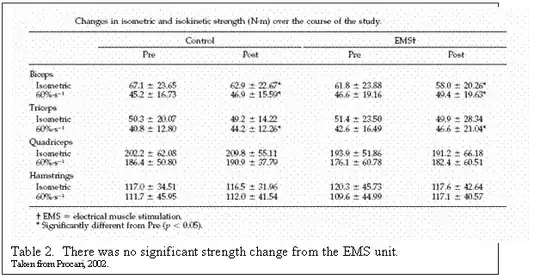
The results showed no significant
changes in weight, percent body fat,
girth or strength of the treatment
areas.
The EMS device did not work
for any of the claims.
In the United States EMS devices are regulated by the FDA:
The use of these electrical devices in
health clubs, beauty salons and figure
salons has been increasing for several
years.
While there are legitimate uses
for both muscle stimulators and
iontophoresis devices, they are
prescription devices and are
misbranded when labeled for lay use.
In addition, muscle stimulators are
misbranded when any of the following
claims are made:
- girth reduction
- loss of inches
- weight reduction
- cellulite removal
- bust development
- body shaping and contouring
- spot reducing


