Yes, although it is generally said that humans do not have estrous cycles in the way most mammals do, there are indeed multiple peer-reviewed studies suggesting that people (not just men, and in some cases other women especially) find ovulating women more attractive. The mechanisms for this are multiple, including both physical and behavioral changes. However, I should emphasize that the effect of each mechanism tested in various experiments is generally small but still enough to be considered statistically significant.
I have no particular expertise in psychology, physiology, etc. so I'm just going to dump some references and findings here without trying to analyze their methodology in depth. The articles I provide full references for are readily available on the open web.
- Roberts, S. Craig, Jan Havlicek, Jaroslav Flegr, Martina Hruskova, Anthony C. Little, Benedict C. Jones, David I. Perrett, and Marion Petrie. "Female facial attractiveness increases during the fertile phase of the menstrual cycle." Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences 271, no. suppl_5 (2004): S270-S272.
This study follows up on earlier research regarding physical attractiveness.
[S]oft tissue traits, such as ears, fingers and breasts, become more symmetrical in the days leading up to ovulation (Manning et al. 1996; Scutt & Manning 1996) and skin colour becomes lighter (Van den Berghe & Frost 1986).
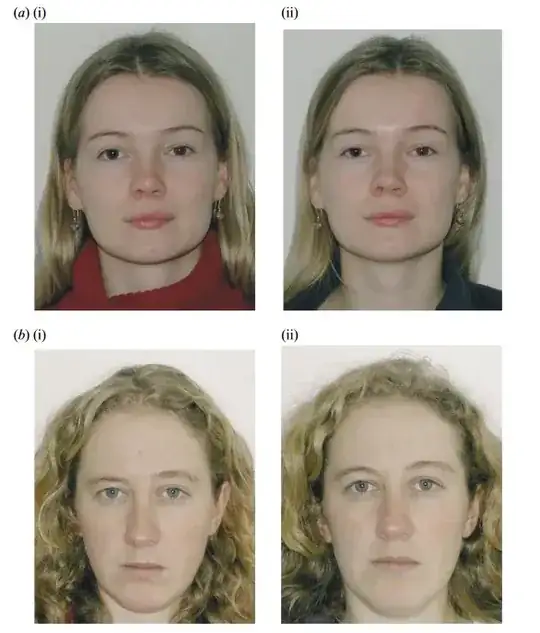
The authors of this particular study used pairs of images of women and had both men and women rate their attractiveness. The article provides a detailed explanation of how the experiment was controlled. Here are sample images provided in the article, in which the women on the right (column "ii") are ovulating. Although I don't personally see a noticeable difference in attractiveness here, I do think the subtle changes in skin tone and symmetry of features described above are perceptible here if you are looking for them.

Here is an excerpt of the authors' conclusions:
Our results indicate that the perceived attractiveness of womens’ faces varies across the menstrual cycle and is higher in the periovulatory than in the luteal phase. This increase in facial attractiveness is clearly subtle and the mean effect size is small. [...] Our results also show that potentially additive information about the stage of the menstrual cycle is available in hairstyle and/or condition (hairstyle was usually but not always constant across the two samples). Surprisingly, this information appears to be used only by other women, suggesting that women may be more aware or better able to discriminate these subtle differences, and that men might fail to detect some available cues to fertility.
- Haselton, Martie G., Mina Mortezaie, Elizabeth G. Pillsworth, April Bleske-Rechek, and David A. Frederick. "Ovulatory shifts in human female ornamentation: Near ovulation, women dress to impress." Hormones and behavior 51, no. 1 (2007): 40-45.
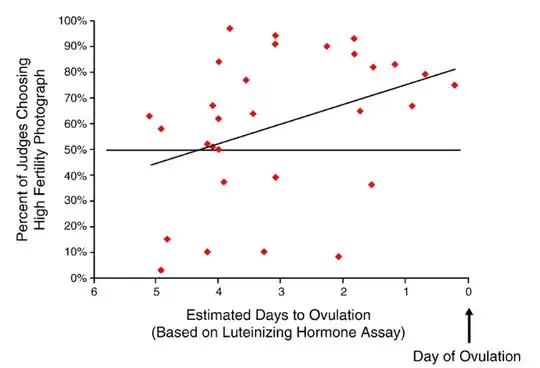
This study focuses on how women dress when they are ovulating. It suggests that these women are more likely to wear "nicer" clothes, lacy tops and short skirts that expose their legs. Male and female judges were asked to look at photos of women and to rate whether the women in the photos were "trying to look attractive". The faces of the women were concealed. Here is a plot of the data showing a correlation between this and their estimated days to ovulation.
- Gildersleeve, Kelly A., Martie G. Haselton, Christina M. Larson, and Elizabeth G. Pillsworth. "Body odor attractiveness as a cue of impending ovulation in women: evidence from a study using hormone-confirmed ovulation." Hormones and behavior 61, no. 2 (2012): 157-166.
In this study, a blind smell test showed that men preferred the body odor of the same women when they were ovulating over when they were not at "above-chance levels" (56%). The study also looked at men's ability to discern the scents of ovulating and non-ovulating women; where that discernment was more accurate, the preference was stronger. A number of earlier studies have also supported the hypothesis that odor plays a role in the attractiveness of ovulating women.
- Bryant, Gregory A., and Martie G. Haselton. "Vocal cues of ovulation in human females." Biology Letters 5, no. 1 (2008): 12-15.
This one documents an increase in the pitch of women's voices just before ovulation. It does not measure whether it effects the perceived attractiveness of the voice.
- Miller, Geoffrey, Joshua M. Tybur, and Brent D. Jordan. "Ovulatory cycle effects on tip earnings by lap dancers: economic evidence for human estrus?" Evolution and Human Behavior 28, no. 6 (2007): 375-381.
This is a small-scale economic study of tip earnings by 18 lap dancers.
We found strong ovulatory cycle effects on tip earnings,moderated by
whether the participants were normally cycling. All women made less
money during their menstrual periods, whether they were on the pill or
not. However, the normally cycling women made much more money during
estrus (about US$354 per shift)—about US$90 more than during the
luteal phase and about US$170 more than during the menstrual phase.
Estrous women made about US$70 per hour, luteal women made about US$50
per hour, and menstruating women made about US$35 per hour.
In their analysis, the authors argue that this is more likely due to "cyclic shifts in women's attractiveness are driving our tip earnings results—rather than the well-documented shifts in sexual receptivity, proceptivity, or selectivity for good genes".
- Haselton, Martie G., and Kelly Gildersleeve. "Can men detect ovulation?." Current directions in psychological science 20, no. 2 (2011): 87-92.
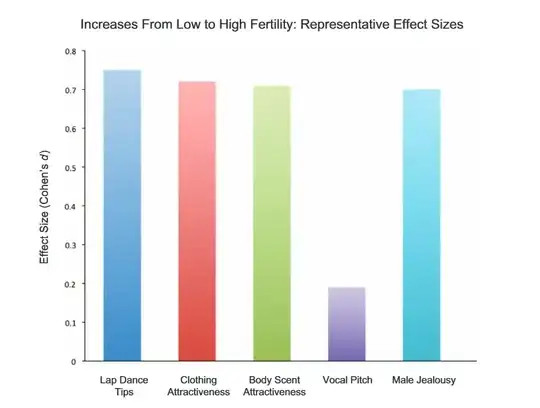
This one is a small meta-study which finds "that there are discernible cues of fertility in women’s social behaviors, body scents, voices, and, possibly, aspects of physical beauty." Here is a graph comparing the results of various studies. It suggests that the effect of a change in voice is small compared to scent and behavior.