We have several servers on AWS EC2 that are not obeying TTL values from DNS. Route tables are set up to us "AmazonProvidedDNS" It appears the the "AmazonProvidedDNS" limits TTL to 60 seconds.
Q: Is this caused by AWS DNS server adjusting the TTL in transit, and is there anything we can do about it?
Notes: - We have employed dnsmasq for now with a min-expiry-ttl of 300; this is not ideal as we'd prefer to obey the TTL rules - Running Centos7, official AMI - but I don't think that's relevant.
Evidence to back up the question.
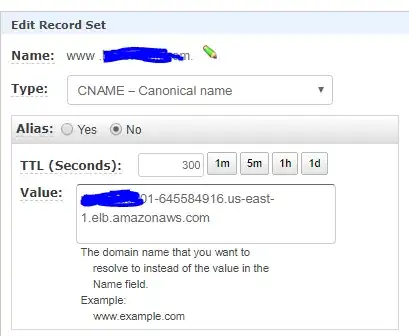
These tests were ran on a domain we have in Route 53 we have a CNAME TTL as 300 seconds. (Outputs below searched and replaced with example ; tests were ran against a real domain we control.)
Have five output below that prove it's AWS DNS:
1) Running the official Centos7 AMI, with no modifications.
This shows incorrect TTL of 60 seconds:
dig www.example.com
; <<>> DiG 9.9.4-RedHat-9.9.4-61.el7 <<>> www.example.com
;; global options: +cmd
;; Got answer:
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 9532
;; flags: qr rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 3, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 1
;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION:
; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;www.example.com. IN A
;; ANSWER SECTION:
www.example.com. 60 IN CNAME example-645584916.us-east-1 .elb.amazonaws.com.
example-645584916.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com. 60 IN A 52.0.228.53
example-645584916.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com. 60 IN A 18.232.11.127
;; Query time: 391 msec
;; SERVER: 10.131.0.2#53(10.131.0.2)
;; WHEN: Wed Jul 25 01:04:00 UTC 2018
;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 140
2) Running the same AMI, with dnsmasq set up but using pointing at AWS DNS as parent.
This shows incorrect TTL of 60 seconds:
dig www.example.com
; <<>> DiG 9.9.4-RedHat-9.9.4-61.el7 <<>> www.example.com
;; global options: +cmd
;; Got answer:
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 57290
;; flags: qr rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 3, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 1
;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION:
; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;www.example.com. IN A
;; ANSWER SECTION:
www.example.com. 60 IN CNAME example-645584916.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com.
example-645584916.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com. 60 IN A 52.0.228.53
example-645584916.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com. 60 IN A 18.232.11.127
;; Query time: 276 msec
;; SERVER: 127.0.0.1#53(127.0.0.1)
;; WHEN: Wed Jul 25 01:03:07 UTC 2018
;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 140
3) Running the same AMI, with dnsmasq set up but using pointing at AWS DNS as parent, with min-cache-ttl.
First request shows incorrect TTL of 60 seconds (as this will have come from AWS), second request shows "min-cache-ttl" of 300 seconds:
dig www.example.com
; <<>> DiG 9.9.4-RedHat-9.9.4-61.el7 <<>> www.example.com
;; global options: +cmd
;; Got answer:
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 26595
;; flags: qr rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 3, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 1
;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION:
; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;www.example.com. IN A
;; ANSWER SECTION:
www.example.com. 60 IN CNAME example-645584916.us-east-1 .elb.amazonaws.com.
example-645584916.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com. 60 IN A 52.0.228.53
example-645584916.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com. 60 IN A 18.232.11.127
;; Query time: 280 msec
;; SERVER: 127.0.0.1#53(127.0.0.1)
;; WHEN: Wed Jul 25 01:25:31 UTC 2018
;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 140
dig www.example.com
; <<>> DiG 9.9.4-RedHat-9.9.4-61.el7 <<>> www.example.com
;; global options: +cmd
;; Got answer:
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 50913
;; flags: qr rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 3, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 1
;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION:
; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;www.example.com. IN A
;; ANSWER SECTION:
www.example.com. 289 IN CNAME example-645584916.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com.
example-645584916.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com. 289 IN A 18.232.11.127
example-645584916.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com. 289 IN A 52.0.228.53
;; Query time: 0 msec
;; SERVER: 127.0.0.1#53(127.0.0.1)
;; WHEN: Wed Jul 25 01:29:02 UTC 2018
;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 143
4) Running the same AMI, with dnsmasq set up (but using pointing at Google DNS as parent).
This shows correct TTL of 300 seconds:
dig www.example.com
; <<>> DiG 9.9.4-RedHat-9.9.4-61.el7 <<>> www.example.com
;; global options: +cmd
;; Got answer:
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 36048
;; flags: qr rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 3, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 1
;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION:
; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 512
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;www.example.com. IN A
;; ANSWER SECTION:
www.example.com. 299 IN CNAME example-645584916.us-east-1 .elb.amazonaws.com.
example-645584916.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com. 59 IN A 18.232.11.127
example-645584916.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com. 59 IN A 52.0.228.53
;; Query time: 295 msec
;; SERVER: 127.0.0.1#53(127.0.0.1)
;; WHEN: Wed Jul 25 01:07:15 UTC 2018
;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 140
5) Running a local Centos7 pointing at our own DNS.
This shows correct TTL of 300 seconds:
dig www.example.com
; <<>> DiG 9.9.4-RedHat-9.9.4-61.el7 <<>> www.example.com
;; global options: +cmd
;; Got answer:
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 7307
;; flags: qr rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 3, AUTHORITY: 13, ADDITIONAL: 27
;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION:
; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;www.example.com. IN A
;; ANSWER SECTION:
www.example.com. 300 IN CNAME example-645584916.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com.
example-645584916.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com. 60 IN A 52.0.228.53
example-645584916.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com. 60 IN A 18.232.11.127
;; Query time: 343 msec
;; SERVER: 10.72.73.31#53(10.72.73.31)
;; WHEN: Wed Jul 25 10:41:02 AEST 2018
;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 936