To start i'm new to Azure.
I've been experimenting with Azure to try and get a basic server up and running with a web server and FTP access.
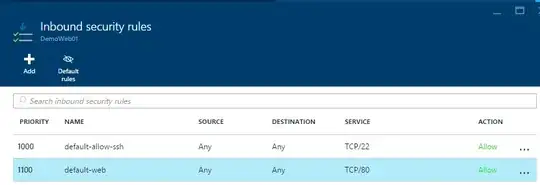
I initially tried to get a Windows server running with IIS but was unable to access the web server via the public IP address. This was created using Resource Manager deployment model. I tried the same with Ubuntu 14.04 with Apache and exactly the same, I couldn't access the web server via the public IP address. In both cases resource manager model was used. End points were configured for port 80 and on windows the firewall was set to accept requests on port 80.
I decided to try setting up Ubuntu using Classic Model, set the endpoints for port 80 (HTTP) and 21(FTP). Once deployed I ssh'd into the server installed Apache2 and vsftpd.
Once they were installed I went to the public IP address and the Apache page displayed. I tested FTP and that worked.
To check if I'd done something wrong with the Resource Manager model deployment I deployed Ubuntu again using Resource Manager Model, set the same endpoint and installed the same software (Apache and vsftp). When I went to the public IP address there was no response.
Has anyone any idea why Azure works like this and how to get the resource managed model deployment to allow access to resources such as a web server vi the public IP address. Is there another level of configuration that is required for Resource Managed deployments?
Thanks