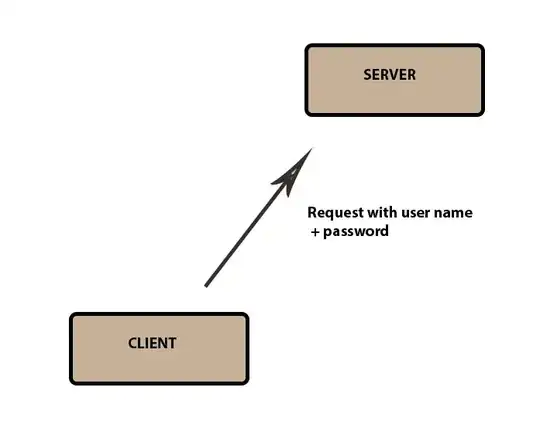
I have the following situation: have a server (ubuntu) running an application. I have a client (only the one client) requesting stuff from that server. To execute the requests, the client has to provide valid credentials.
Now someone could track the traffic and sniff the credentials. Therefore I need to secure the connection. I guess HTTPS and certificates are the way to go here. But I have a basic understandig problem here. Do I need to generate a certificate on the server and give it to the client, so he can sign his requests? Or how is this working?
I really only have this one server and one client. No other client should ever be able to talk to my server. (And I cannot restrict the requests to the IP of the client because it is changing)