Diuretics
Types
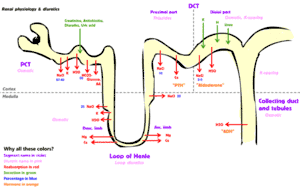
High ceiling/loop diuretic
Inhibit Na+/K+/2Cl symporter in ascending limb of loop of Henle, preventing reabsorption and thereby increasing urinary excretion of sodium, chloride, and potassium
- Furosemide
- Ethacrynic acid
- Torsemide
- Bumetanide
- 40mg furosemide = 20 mg torsemide = 1mg bumetanide = 50 mg ethacrynic acid
Thiazides
Act on the distal convoluted tubule and inhibit the sodium-chloride symporter
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
Inhibit the enzyme carbonic anhydrase in the proximal convoluted tubule
Potassium-sparing diuretics
- Aldosterone antagonists
- Epithelial sodium channel blockers:
Osmotic diuretics
Increase osmolality and work primarily by expanding extracellular fluid and plasma volume, therefore increasing blood flow to the kidneys
- Mannitol
- Glucose (e.g. during hyperglycemia)
See Also
- Antihypertensive medications
This article is issued from Wikem. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.