Ascending cholangitis
Background
- Also known as "acute cholangitis" or simply "cholangitis"
- Requires the presence of biliary obstruction and infected biliary tract
Anatomy & Pathophysiology
- Gallstones are classified as cholesterol stones and pigmented stones (black and brown), and are present in approx 20% of females and 8% of males in the United States
- These stones cause the majority of all biliary tract problems, and depending on where the stone become impacted, specific problems occur.
- Bile flows out the gallbladder, down the cystic duct into the common bile duct, and ultimately into the 1st portion of the duodenum.
Gallbladder disease types
.png.webp)
Gallbladder anatomy (overview).

Gallbladder anatomy
Causes
- Choledocholithiasis
- Biliary tract stricture
- Compression by malignant disease
Clinical Features
- Charcot's Triad: Fever + jaundice + RUQ pain
- Occurs in ~50%
- Reynold's Pentad: The triad + altered mental status + hypotension
- Occurs in <5%
- Hypotension may be the only presenting sign in elderly patients
Differential Diagnosis
RUQ Pain
- Gallbladder disease
- Symptomatic cholelithiasis (biliary colic)
- Choledocholithiasis
- Acute cholecystitis
- Ascending cholangitis
- Acalculous cholecystitis
- Peptic ulcer disease with or without perforation
- Pancreatitis
- Acute hepatitis
- Pyelonephritis
- Pneumonia
- Kidney stone
- Pancreatitis
- GERD
- Appendicitis (retrocecal)
- Pyogenic liver abscess
- Fitz-Hugh-Curtis Syndrome
- Hepatomegaly due to CHF
- Herpes zoster
- Myocardial ischemia
- Bowel obstruction
- Pulmonary embolism
- Abdominal aortic aneurysm
Evaluation

MRCP image of two stones in the distal common bile duct
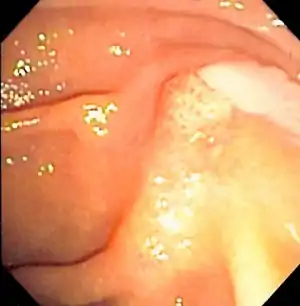
Duodenoscopy image of pus extruding from Ampulla of Vater, indicative of cholangitis.
Work-up
- Labs
- CBC: Leukocytosis with neutrophil predominance
- LFTs: Elevated alk phos and conjugated bilirubin
- GGT elevation much more sensitive than alk phos
- Blood cultures
- Imaging
- RUQ Ultrasound
- Dilatation of CBD ( > 6mm) and presence of choledocholithiasis
- May miss small CBD stones and in acute cases CBD may not have had time to dilate
- RUQ Ultrasound
- ERCP
- Should be obtained to confirm the diagnosis and for possible intervention
Management
- Aggressive sepsis resuscitation
Antibiotics
Coverage is targeted at E. coli, Enterococcus, Bacteroides, and Clostridium (anerobic)
- Metronidazole 500mg IV q8hrs PLUS Ciprofloxacin 400mg IV q12hrs
- Piperacillin/Tazobactam 4.5g IV q8hrs
- Imipenem/Cilastin 500mg IV q6hrs
- Doripenem 500mg IV q8hrs
- Meropenem 1g IV q8hrs
- expand coverage for MRSA if severe sepsis or septic shock
- Vancomycin 15-20mg/kg PLUS any of the following options
Consultation
- Involvement with GI for ERCP and general surgery for acute cholecystectomy is necessary for source control and biliary decompression
Disposition
- Admit
See Also
- Gallbladder Disease (Main)
References
This article is issued from Wikem. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.