For permutations, rcppalgos is great. Unfortunately, there are 479 million possibilities with 12 fields which means that takes up too much memory for most people:
library(RcppAlgos)
elements <- 12
permuteGeneral(elements, elements)
#> Error: cannot allocate vector of size 21.4 Gb
There are some alternatives.
Take a sample of the permutations. Meaning, only do 1 million instead of 479 million. To do this, you can use permuteSample(12, 12, n = 1e6). See @JosephWood's answer for a somewhat similar approach except he samples out to 479 million permutations ;)
Build a loop in rcpp to evaluate the permutation on creation. This saves memory because you would end up building the function to return only the correct results.
Approach the problem with a different algorithm. I will focus on this option.
New algorithm w/ constraints
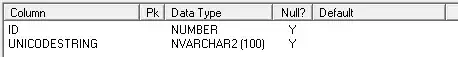
Segments should be 26
We know that each line segment in the star above needs to add up to 26. We can add that constraint to generating our permutations - give us only combinations that add up to 26:
# only certain combinations will add to 26
lucky_combo <- comboGeneral(12, 4, comparisonFun = '==', constraintFun = 'sum', limitConstraints = 26L)
ABCD and EFGH groups
In the star above, I have colored three groups differently : ABCD, EFGH, and IJLK. The first two groups also have no points in common and are also on line segments of interest. Therefore, we can add another constraint: for combinations that add up to 26, we need to ensure ABCD and EFGH have no number overlap. IJLK will be assigned the remaining 4 numbers.
library(RcppAlgos)
lucky_combo <- comboGeneral(12, 4, comparisonFun = '==', constraintFun = 'sum', limitConstraints = 26L)
two_combo <- comboGeneral(nrow(lucky_combo), 2)
unique_combos <- !apply(cbind(lucky_combo[two_combo[, 1], ], lucky_combo[two_combo[, 2], ]), 1, anyDuplicated)
grp1 <- lucky_combo[two_combo[unique_combos, 1],]
grp2 <- lucky_combo[two_combo[unique_combos, 2],]
grp3 <- t(apply(cbind(grp1, grp2), 1, function(x) setdiff(1:12, x)))
Permute through the groups
We need to find all permutations of each group. That is, we only have combinations that add up to 26. For example, we need to take 1, 2, 11, 12 and make 1, 2, 12, 11; 1, 12, 2, 11; ....
#create group perms (i.e., we need all permutations of grp1, grp2, and grp3)
n <- 4
grp_perms <- permuteGeneral(n, n)
n_perm <- nrow(grp_perms)
# We create all of the permutations of grp1. Then we have to repeat grp1 permutations
# for all grp2 permutations and then we need to repeat one more time for grp3 permutations.
stars <- cbind(do.call(rbind, lapply(asplit(grp1, 1), function(x) matrix(x[grp_perms], ncol = n)))[rep(seq_len(sum(unique_combos) * n_perm), each = n_perm^2), ],
do.call(rbind, lapply(asplit(grp2, 1), function(x) matrix(x[grp_perms], ncol = n)[rep(1:n_perm, n_perm), ]))[rep(seq_len(sum(unique_combos) * n_perm^2), each = n_perm), ],
do.call(rbind, lapply(asplit(grp3, 1), function(x) matrix(x[grp_perms], ncol = n)[rep(1:n_perm, n_perm^2), ])))
colnames(stars) <- LETTERS[1:12]
Final Calculations
The last step is to do the math. I use lapply() and Reduce() here to do more functional programming - otherwise, a lot of code would be typed six times. See the original solution for a more thorough explanation of the math code.
# creating a list will simplify our math as we can use Reduce()
col_ind <- list(c('A', 'B', 'C', 'D'), #these two will always be 26
c('E', 'F', 'G', 'H'), #these two will always be 26
c('I', 'C', 'J', 'H'),
c('D', 'J', 'G', 'K'),
c('K', 'F', 'L', 'A'),
c('E', 'L', 'B', 'I'))
# Determine which permutations result in a lucky star
L <- lapply(col_ind, function(cols) rowSums(stars[, cols]) == 26)
soln <- Reduce(`&`, L)
# A couple of ways to analyze the result
rbind(stars[which(soln),], stars[which(soln), c(1,8, 9, 10, 11, 6, 7, 2, 3, 4, 5, 12)])
table(Reduce('+', L)) * 2
2 3 4 6
2090304 493824 69120 960
Swapping ABCD and EFGH
At the end of the code above, I took advantage that we can swap ABCD and EFGH to get the remaining permutations. Here is the code to confirm that yes, we can swap the two groups and be correct:
# swap grp1 and grp2
stars2 <- stars[, c('E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'I', 'J', 'K', 'L')]
# do the calculations again
L2 <- lapply(col_ind, function(cols) rowSums(stars2[, cols]) == 26)
soln2 <- Reduce(`&`, L2)
identical(soln, soln2)
#[1] TRUE
#show that col_ind[1:2] always equal 26:
sapply(L, all)
[1] TRUE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE
Performance
In the end, we evaluated only 1.3 million of the 479 permutations and only only shuffled through 550 MB of RAM. It takes around 0.7s to run
# A tibble: 1 x 13
expression min median `itr/sec` mem_alloc `gc/sec` n_itr n_gc
<bch:expr> <bch> <bch:> <dbl> <bch:byt> <dbl> <int> <dbl>
1 new_algo 688ms 688ms 1.45 550MB 7.27 1 5